Edwin Pascal Alyea, MD
- Instructor in the Department of Medicine

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/edwin-pascal-alyea-md
Calcitriol dosages: 0.25 mcg
Calcitriol packs: 30 caps, 60 caps, 90 caps, 120 caps, 180 caps, 270 caps, 360 caps

Buy calcitriol 0.25 mcg on line
Liu Y, Wu D, Lao D, et al: Laser-assisted era of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Ogonuki N, Inoue K, Yamamoto Y, et al: Early death of mice cloned from somatic cells. Sharp J, Frame J, Siegenthaler M, et al: Human embryonic stem cell-derived oligodendrocyte progenitor cell transplants improve restoration after cervical spinal twine harm. Yu J, Hu K, Smuga-Otto K, et al: Human induced pluripotent stem cells freed from vector and transgene sequences. Maekawa M, Yamaguchi K, Nakamura T, et al: Direct reprogramming of somatic cells is promoted by maternal transcription issue Glis1. Seki T, Yuasa S, Oda M, et al: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from human terminally differentiated circulating T cells. Maherali N, Ahfeldt T, Rigamonti A, et al: A high-efficiency system for the era and examine of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Okita K, Nakagawa M, Hyenjong H, et al: Generation of mouse induced pluripotent stem cells with out viral vectors. Kaji K, Norrby K, Paca A, et al: Virus-free induction of pluripotency and subsequent excision of reprogramming components. Woltjen K, Hamalainen R, Kibschull M, et al: Transgene-free manufacturing of pluripotent stem cells utilizing piggyBac transposons. Nishimura K, Sano M, Ohtaka M, et al: Development of defective and persistent Sendai virus vector: a unique gene delivery/expression system ideal for cell reprogramming. Hou P, Li Y, Zhang X, et al: Pluripotent stem cells induced from mouse somatic cells by small-molecule compounds. Corti S, Faravelli I, Cardano M, Conti L: Human pluripotent stem cells as tools for neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disease modeling and drug discovery. Strick-Marchand H, Dusseaux M, Darche S, et al: A novel mouse model for secure engraftment of a human immune system and human hepatocytes. Shreeve J: the opposite stem-cell debate: to take a look at the potential curative powers of human embryonic stem cells, biologists need to inject them into lab animals. Creating such chimeras makes excellent sense, to a point: a sheep with a human liver Araki R, Uda M, Hoki Y, et al: Negligible immunogenicity of terminally differentiated cells derived from induced pluripotent or embryonic stem cells. Schuldiner M, Yanuka O, Itskovitz-Eldor J, et al: Effects of eight progress factors on the differentiation of cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Durai S, Mani M, Kandavelou K, et al: Zinc finger nucleases: custom-designed molecular scissors for genome engineering of plant and mammalian cells. Amabile G, Meissner A: Induced pluripotent stem cells: present progress and potential for regenerative drugs. Raya A, Rodriguez-Piza I, Guenechea G, et al: Disease-corrected haematopoietic progenitors from Fanconi anaemia induced pluripotent stem cells. Yu D, Swaroop M, Wang M, et al: Niemann-Pick illness sort c: induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuronal cells for modeling neural illness and evaluating drug efficacy. Brustle O, Choudhary K, Karram K, et al: Chimeric brains generated by intraventricular transplantation of fetal human mind cells into embryonic rats. Windrem M, Schanz S, Guo M, et al: Neonatal chimerization with human glial progenitor cells each remyelinates and rescues the in any other case lethally hypomyelinated shiverer mouse. Glass R, Synowitz M, Kronenberg G, et al: Glioblastoma-induced attraction of endogenous neural precursor cells is related to improved survival. Obenaus A, Dilmac N, Tone B, et al: Long-term magnetic resonance imaging of stem cells in neonatal ischemic injury. Rosen C, Shezen E, Aronovich A, et al: Preconditioning allows engraftment of mouse and human embryonic lung cells, enabling lung repair in mice. Kamao H, Mandai M, Okamoto S, et al: Characterization of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium cell sheets aiming for scientific application. Mavilio F, Pellegrini G, Ferrari S, et al: Correction of junctional epidermolysis bullosa by transplantation of genetically modified epidermal stem cells.
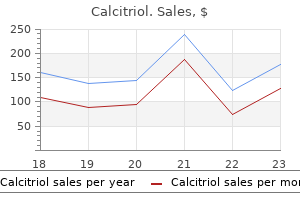
0.25 mcg calcitriol order amex
Differential regulation of nitric oxide synthase-2 and arginase-1 by kind 1/type 2 cytokines in vivo: granulomatous pathology is shaped by the pattern of L-arginine metabolism. Interleukin-13 induces tissue fibrosis by selectively stimulating and activating reworking development factor beta(1). Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13enhanced reworking progress factor-beta2 production in cultured human bronchial epithelial cells is attenuated by interferon-gamma. Differential monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and chemokine receptor 2 expression by murine lung fibroblasts derived from Th1- and Th2-type pulmonary granuloma fashions. Interleukin-13 stimulates the proliferation of lung myofibroblasts via a sign transducer and activator of transcription-6-dependent mechanism: a potential mechanism for the development of airway fibrosis in bronchial asthma. Leukotrienes mediate murine bronchopulmonary hyperreactivity, inflammation, and part of mucosal metaplasia and tissue damage induced by recombinant murine interleukin-13. Direct results of interleukin-13 on epithelial cells trigger airway hyperreactivity and mucus overproduction in bronchial asthma. Effect of various penicillin derivatives on complement elements in human serum. Blackley and the development of hay fever as a disease of civilization in the nineteenth century. A second research of the behaviour and fate of skin homografts in rabbits; a report to the War Wounds Committee of the Medical Research Council. Role of persistence of antigen and oblique recognition in the maintenance of tolerance to renal allografts. Characterization of a clonal assay and willpower of the size of clones derived from single precursors. Quantifying the frequency of alloreactive T cells in vivo: new answers to an old query. Limiting dilution evaluation of alloreactive T-cell status and distribution throughout allograft rejection. The position of peptides in T cell alloreactivity is decided by self-major histocompatibility advanced molecules. The crystal constructions of K(bm1) and K(bm8) reveal that delicate changes within the peptide environment impression thermostability and alloreactivity. Alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes concentrate on specific major histocompatibility complex-bound peptides. Induction of minor alloantigen-specific T cell subsets in vivo: recognition of processed antigen by helper however not by cytotoxic T cell precursors. Identification of classical minor histocompatibility antigen as cell-derived peptide. Cellular peptide composition ruled by main histocompatibility advanced class I molecules. Feasibility of immunotherapy of relapsed leukemia with ex vivogenerated cytotoxic T lymphocytes particular for hematopoietic systemrestricted minor histocompatibility antigens. Identification of a graft versus host disease-associated human minor histocompatibility antigen. The immunogenicity of a new human minor histocompatibility antigen outcomes from differential antigen processing. Differences that matter: main cytotoxic T cell-stimulating minor histocompatibility antigens. The relevance of minor histocompatibility antigens in solid organ transplantation. Role of perforin-mediated cell apoptosis in murine fashions of infusion-induced bone marrow failure. Decreased immunogenicity of a transplantation antigen in hosts sensitized to other isoantigens of its cellular vehicle. Antigen competition in cytotoxic T cell response to minor histocompatibility antigens. The preferential cytolytic T lymphocyte resonse to immunodominant minor histocompatibility antigen peptides. Immunodominance of H60 is brought on by an abnormally excessive precursor T cell pool directed towards its unique minor histocompatibility antigen peptide. Immunodominance within the graft-vs-host illness T cell response to minor histocompatibility antigens. In vitro cell-mediated immune responses to the male specific (H-Y) antigen in mice.
Syndromes
- Cause sores or cracks in the walls of the vagina
- Undercooked meats or eggs
- Receive creams to treat skin changes around the nipple
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Your valve has developed an infection (infectious endocarditis)
- Tall height
- Convulsions
- Pregnancy (third trimester)
Buy genuine calcitriol line
The nephron from the renal corpuscle to the collecting duct is derived from the metanephric blastema, whereas the accumulating system and ureter are derived from the ureteric bud. Development of the metanephric kidney depends on mutual inductive signals from the metanephric blastema and the ureteric bud. The vesicle remodels itself into a tubule, the proximal finish of which attaches to the ureteric bud, whereas the distal end becomes related to vascular precursors of the glomerulus. Signals from the metanephric mesoderm cause the ureteric bud to department, forming the accumulating system. During the middle of the embryonic interval, its lumen is obliterated by proliferation of the endoderm-derived lining cells, however cell death (a regular developmental process in many areas of the human embryo) reestablishes the lumen by early fetal life. Growth of the dorsal wall of the abdomen surpasses that of the ventral wall, leading to the larger curvature and driving a clockwise rotation of the gut that brings the larger curvature (original dorsal surface) to the left and the lesser curvature (original ventral surface) to the right. As a results of differential progress, the cardiac region (cranial) of the stomach moves inferiorly and to the left, and the pyloric (caudal) finish moves superiorly and to the best. Ultimately this rearrangement ends in the simply about horizontal axis seen in the grownup stomach. It quickly elongates into a loop, the bend of which is towards the ventral body wall. As the stomach rotates to the best, so does the duodenal loop, bringing it to lie against the dorsal wall of the physique cavity. There it fuses with the dorsal wall, and most of it involves lie in a retroperitoneal position. As in the esophagus, the duodenal lumen is transiently obliterated by growth of the endoderm-derived lining cells till the start of the fetal interval. The elongating midgut types a U-shaped loop consisting of a cranial and a cadual limb. While herniated, the loop rotates ninety degrees counterclockwise when seen from the ventral surface of the embryo. At the same time growth and elongation create several further subloops within the cranial portion of the U-shaped loop; these later give rise to the jejunum and ileum. Chapter3-BasicEmbryology 37 develop from coelomic mesoderm (cortex) and neural crest cells (medulla) which have turn into associated in the belly cavity, cephalic to the ultimate place of the kidneys. The urogenital sinus is an endoderm-lined cavity from which are derived the epithelium of the urinary bladder, all of the female urethra, and most of the male urethra. The muscular coats and connective tissue components of all of those structures are of splanchnic mesoderm origin. Clinically, one determines the beginning of gestation by counting from the date of the last menstrual period. With respect to human embryology, the time period embryo means "an unborn human within the first eight weeks" from fertilization. It is believed that during the first 2 weeks of improvement the embryo is comparatively insensitive to the motion of agents that trigger congenital malformations (teratogens). During this 2-week interval, defects may develop after treatment with the teratogenic agent if for some reason it remains available to the embryo throughout the period-for instance, because of gradual metabolism or excretion. It is through the third to eighth week of improvement, however, that morphogenesis of most organ methods begins and, for many techniques, ends. This is the portion of the embryonic period by which the organs, and due to this fact the embryo as a whole, are most sensitive to the actions of teratogens. For instance, a kidney will fail to develop provided that, throughout morphogenesis, the ureteric bud fails to send the right alerts to the metanephric blastema. Moreover, a limb might be abnormally foreshortened only if lengthy bones fail to kind throughout that point when the bony components are as a outcome of endure their major morphogenesis. Therefore weeks 3 to eight of the embryonic interval represent the crucial interval in human improvement with regard to the action of teratogenic brokers. An example of such an organ is the mind, which displays the longest developmental interval of any organ; it continues both physical and functional growth throughout the fetal period and beyond, nicely after delivery. In contrast with the mind, nonetheless, morphogenesis of most different organ techniques is actually complete by the top of the embryonic interval. Peters H: Migration of gonocytes into the mammalian gonad and their differentiation. In Yoshinga K, Mori T, editors: Development of preimplantation embryos and their surroundings, New York, 1989, Alan R Liss, pp 21�32.
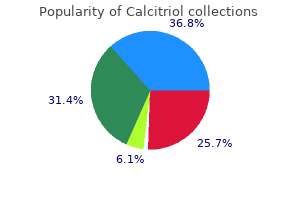
0.25 mcg calcitriol buy mastercard
Randomized, double-blind study of denosumab versus zoledronic acid within the therapy of bone metastases in sufferers with advanced cancer (excluding breast and prostate cancer) or a quantity of myeloma. Denosumab versus zoledronic acid for therapy of bone metastases in males with castration-resistant prostate cancer: a randomised, double-blind examine. Elevated serum B lymphocyte stimulator levels in patients with systemic immune-based rheumatic ailments. Conatumumab, a completely human mAb against dying receptor 5 for the therapy of most cancers. Stabilization of the bioactivity of tumor necrosis issue by its soluble receptors. Distinct roles in lymphoid organogenesis for lymphotoxins a and b revealed in lymphotoxin b-deficient mice. Lymphotoxins and cytomegalovirus cooperatively induce interferon-, establishing host-virus d�tente. Lymphotoxin-mediated crosstalk between B cells and splenic stroma promotes the initial type I interferon response to cytomegalovirus. Reversal of virus-induced systemic shock and respiratory failure by blockade of the lymphotoxin pathway. Lymphotoxin-alphadeficient mice make delayed, but efficient, T and B cell responses to influenza. The lymphotoxin beta receptor is critically concerned in controlling infections with the intracellular pathogens Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Listeria monocytogenes. Secreted lymphotoxin-alpha is important for the management of an intracellular bacterial infection. Membrane lymphotoxin contributes to anti-leishmanial immunity by controlling structural integrity of lymphoid organs. Macrophage inflammatory proteins 1 and 2: members of a novel superfamily of cytokines. Traffic alerts for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Chemokines, sphingosine-1�phosphate, and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Chemokines in innate and adaptive host defense: fundamental chemokinese grammar for immune cells. A receptor for the malarial parasite Plasmodium vivax: the erythrocyte chemokine receptor. Molecular uncoupling of fractalkinemediated cell adhesion and signal transduction. Cutting edge: novel human dendritic cell- and monocyte-attracting chemokine-like protein recognized by fold recognition methods. Regulation of protein perform by glycosaminoglycans-as exemplified by chemokines. Interaction of chemokines and glycosaminoglycans: a model new twist in the regulation of chemokine function with opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Glycosaminoglycan binding and oligomerization are important for the in vivo exercise of sure chemokines. Identification of human macrophage inflammatory proteins 1alpha and 1beta as a local secreted heterodimer. Structure, operate and physiological consequences of virally encoded chemokine seven transmembrane receptors. D6 and the atypical chemokine receptor household: novel regulators of immune and inflammatory processes. Chemokine class differences in binding to the Duffy antigen-erythrocyte chemokine receptor. The Duffy antigen receptor for chemokines transports chemokines and helps their promigratory exercise. Chemokine scavenger D6 is expressed by trophoblasts and aids the survival of mouse embryos transferred into allogeneic recipients. The beta-chemokine receptor D6 is expressed by lymphatic endothelium and a subset of vascular tumors.
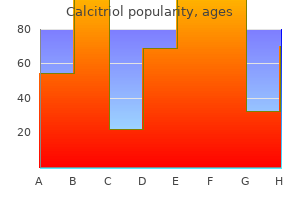
Calcitriol 0.25 mcg buy amex
Arola L, Palou A, Remesar X, Alemany M: Effects of 24 hour starvation on plasma composition in 19 and 21 day pregnant rats and their foetuses. Mori M, Li G, Abe I, et al: Lanosterol synthase mutations trigger ldl cholesterol deficiency�associated cataracts in the Shumiya cataract rat. Chevallier F: Transferts et synth�se du ldl cholesterol chez le rat au cours de sa croissance. Gaoua W, Wolf C, Chevy F, et al: Cholesterol deficit but not accumulation of aberrant sterols is the main explanation for the teratogenic exercise in the SmithLemli-Opitz syndrome animal model. Yoshida S, Wada Y: Transfer of maternal ldl cholesterol to embryo and fetus in pregnant mice. Nakai T, Tamai T, Yamada S, et al: Plasma lipids and lipoproteins of Japanese adults and umbilical cord blood. Diaz M, Leal C, Ramon y Cajal J, et al: Cord blood lipoprotein-cholesterol: Relationship of birth weight and gestational age of newborns. A novel lipoprotein receptor of the low density lipoprotein receptor family predominantly expressed in mind. Coming from a protected and thermoneutral environment, the newborn infant is suddenly exposed to "cool" environment, the place survival depends on selfgeneration of enough warmth to keep warm. The growth of the ability to regulate body temperature regardless of the temperature of the surroundings (and through this to ensure that exercise of the organism is fixed and high) apparently was a needed step within the evolution of so-called larger animals. A requirement for this improvement was that newborns be endowed with a physiologic capability to produce the warmth important for survival. To accomplish this, an organ was developed with out parallel in ectothermic animals, an organ endowed with the perform of producing warmth exactly when required, not least around the time of start. Its function as a heat producer within the cold1 and in newborns2,3 was first described solely slightly more than 50 years in the past. However, during subsequent years, understanding has grown in regards to the events responsible for the heat production in that tissue,4-10 and at present, researchers are actively elucidating mechanisms underlying the recruitment processes in brown adipose tissue. This protein functions as a regulated protonophore via the mitochondrial membrane. The identification of this protein consolidated, in some ways, research on brown adipose tissue. Thus an outline of the function and destiny of this protein should be a central concern in a review on the perinatal recruitment of brown adipose tissue. The only different available methods to decide the presence of brown adipose tissue (but not its acute activity) are invasive and therefore also inappropriate for intensive research. Magnetic resonance imaging and infrared thermography methods are actually being evaluated and can hopefully provide more suitable technique of research in the close to future. There are reports suggesting sure levels of abundance in kids, however these are unable to give dependable data, because the environmental temperature has not been appropriate for optimizing the visibility of brown adipose tissue. Significant differences in perinatal development of brown fats (and many different characteristics) have been documented among newborns of different species. As discussed afterward, improvement of brown adipose tissue in these newborns is a slow course of that begins simply earlier than delivery and reaches its most some days after delivery. The major driving force for this recruitment might be the (comparatively) low environmental temperature coupled with the try by these newborns to activate processes to oppose hypothermia. The morphologic and ultrastructural improvement of the tissue in these animals has been described. In species with immature newborns, the recruitment process in brown adipose tissue starts only when the central control system has developed, after which processes happen that seem much like these elicited instantly after start within the altricial newborns. These newborns are born with well-developed brown adipose tissue, which tends to atrophy postnatally. It is unknown how this intrauterine recruitment of brown adipose tissue is completed. Certain small newborns, such because the guinea pig,34 belong to this group, however extra apparent members are the newborns of many larger species, such as lambs,35-37 goats,38 calves,39,forty and musk oxen. Although born in a considerably developed state, the human infant has a number of traits of immaturity and probably is most akin to the altricial newborns-specifically, human perinatal brown adipose tissue improvement is similar to that found within the new child rat pup. Experiments concerning the operate of most body organs are helped from a practical standpoint by the fact that most organs are anatomically well-defined entities with a single localization in the body and with structurally homogeneous and secure cells.
Order generic calcitriol line
Thearrowspointingdownfromthe decrease mind stem symbolize pathways to mononeurons and dorsal horn neurons within the spinal cord; the latter can suppress enter from the warm afferents. The inhibitory action on the efferents to warmth loss effectors is exerted by way of interneurons. Activation of warm receptors excites the efferents to the warmth loss effectors, concurrently inhibiting (through interneurons) the efferents to the effectors for heat manufacturing. The varied effector neurons might obtain completely different combinations of thermal afferents. Deviations of such a representative temperature from an empirically attained regular value may be described as a set-point displacement or, extra specifically, as a deviation of the threshold temperatures for the respective control actions. After a brief evaluate of the relationship between metabolic price and environmental temperature, management of heat production and warmth loss are mentioned separately. In the neonates of all homeothermic species studied thus far (except for the ground squirrel and golden hamster, which are hibernators), a cold-induced increase in metabolic fee has been demonstrated instantly after birth. As demonstrated by a number of investigators, oxygen uptake (directly proportional to thermogenesis) is distinctly larger at 28� C ambient temperature than at 32� to 35� C, even through the first few hours of life. Depending on the species, this cold-induced metabolic response will increase to a higher or lesser extent through the first week of life. Under environmental situations that permit the control actions to attain ineffective levels, the deep body temperature will stabilize at a worth typical for the species (if sufficient time is allowed to attain steady-state warmth flow). Green space indicates range of mean pores and skin temperatures related for the comparison of shivering threshold values. Within the thermoneutral zone, heat manufacturing (corresponding to the at-rest [basal] metabolic rate) is in equilibrium with heat loss only if pores and skin blood flow is progressively decreased because the temperature decreases from the higher finish of the thermoneutral zone (T3) to its lower finish (T2). At temperatures lower than T2, body temperature could be saved constant only if heat loss is strictly compensated for by increasing thermoregulatory warmth production (cold-induced thermogenesis). At temperatures greater than T3, thermal equilibrium can be achieved solely by a further warmth loss mechanism-the secretion and evaporation of sweat. The time period thermoneutral zone was initially defined solely with respect to metabolic price, and a few problems arose concerning its use in perinatal physiology. In small premature infants (1 kg), the decrease limit of the thermoneutral zone could additionally be as high as 35� C. It is thus extraordinarily tough to present exact standard values for the thermoneutral zone in neonates. Oxygen uptake values of 15 mL/kg/minute measured at an ambient temperature of 23� C1 and of sixteen. For comparison, in well-trained younger adults, summit oxygen consumption could improve to five instances the extent at rest-that is, to 17 to 20 mL/ kg/minute, when the environmental temperature is maintained at 0� to 5� C. The upkeep of constant physique temperature requires that heat loss and warmth manufacturing be equal in the steady state. Three principal modes of heat manufacturing are answerable for the rise of warmth production with decreasing environmental temperature: (1) voluntary muscle exercise, (2) involuntary tonic or rhythmic muscle activity (the latter may be manifest as shivering or could also be invisible and detectable solely by electromyography), and (3) nonshivering thermogenesis. The existence of nonshivering thermogenesis was initially evidenced by the demonstration of a cold-induced enhance in oxygen uptake that continued after neuromuscular blockade with curare. In contrast, nonshivering thermogenesis is a vital and efficient mechanism of warmth manufacturing within the neonates of many mammalian species, including human infants. In comparison with nonshivering thermogenesis, shivering is a much less economical type of warmth manufacturing in that it inevitably will increase convective warmth loss because of the body oscillations. This economical aspect turns into extra important in smaller organisms (high surface-to-mass ratio) with poorer thermal insulation. During the early Sixties it was advised that brown adipose tissue was the primary website of nonshivering thermogenesis. In distinction, on day 12 of life, publicity to the same ambient temperatures (16� and 8� C) evokes bursts of electrical muscle activity which are accompanied by seen muscle oscillations. One might conclude, due to this fact, that the shivering mechanism is properly developed on the time of start however is often suppressed by nonshivering thermogenesis. Shivering has also been observed in human neonates with extreme hypothermia after birth. It has thus been concluded that the shivering threshold is displaced in neonates to a decrease physique temperature as compared with the adult.
Pseudotsuga menziesii (Oregon Fir Balsam). Calcitriol.
- How does Oregon Fir Balsam work?
- What is Oregon Fir Balsam?
- Are there safety concerns?
- Dosing considerations for Oregon Fir Balsam.
- Burns, sores, cuts, heart and chest pain, tumors, and other conditions.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96500
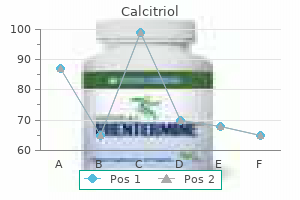
0.25 mcg calcitriol buy with visa
SkeletalMuscle Cardiac muscle develops from splanchnic mesoderm adjacent to the pericardial or transverse portion of the intraembryonic coelom. Rather, the myoblasts differentiate as discrete cells, with intently applied end-to-end junctions, which persist as the grownup intercalated disk. They type a layer across the endothelial tube of the heart, which finally becomes the myocardial or muscular wall of the guts. SmoothMuscle Mesenchyme cells which are to develop into skeletal muscle elongate and lose their a quantity of processes. These myotubes start producing actin and myosin myofilaments, which will increase girth. The skeletal muscle tissue of the pinnacle and neck develop from paraxial mesoderm represented by somitomeres in the early embryo. Somites themselves are attention-grabbing structures-serially repeated paired blocks of condensed (closely packed) paraxial mesoderm cells. Approximately forty four pairs of somites finally develop in humans, beginning between day 19 and day 21. Chondroblasts aggregate, condense, and start to produce collagen fibers and floor substance. In the embryo, bone tissue is formed in either of two distinct methods, relying on the site and type of bone development. The first is de novo bone formation, during which mesoderm cells (or, within the case of some cranium bones, neural crest cells) first condense (pack) into sheets or membranes. Cells in these sheets then differentiate into osteoblasts, which secrete prebone or osteoid. Osteoid is the extracellular matrix onto which hydroxyapatite crystals (a unique calcium phosphate mineral) type. Once the mineral is present and built-in into the collagen of the matrix, the tissue is taken into account to be bone. This type of bone formation is identified as Chapter3-BasicEmbryology 35 intramembranous ossification as a outcome of the osteogenesis occurs within these sheets or membranes of condensed mesenchyme. The second method during which bone forms within the embryo is called endochondral ossification. As implied by the name, bone types in this case solely in sites where preexisting cartilage fashions are discovered. Rather, bone replaces the preexisting cartilage mannequin in a sequence of steps, as follows. Cartilage cells hypertrophy and calcify in an space where bone is to form-that is, they turn out to be large and bear metabolic modifications, which result in infiltration of the encompassing cartilage extracellular matrix with insoluble calcium salts. At the identical time, native osteoblasts begin to produce osteoid, which then turns into mineralized as described in intramembranous ossification. Once bone has shaped within the embryo, it might be transformed by changes in the steadiness between addition of extra bone by osteoblasts and removing of bone by osteoclasts. A groove, the respiratory (laryngotracheal) diverticulum, arises as an evagination of the ventral surface of the foregut, near the region destined to become the abdomen. As the foregut elongates, a wedge of mesoderm, the tracheoesophageal septum, separates the foregut (portion that can become the esophagus) from the lengthy run lungs. This early affiliation of growing lung and stomach results in the occasional discovering of ectopic lung and cartilage tissue close to the esophagogastric junction. On the left facet, two secondary bronchi provide the creating superior and inferior lobes of the left lung. On the best facet, the inferior secondary bronchus divides into two bronchi, offering a total of three secondary bronchi to supply the three lobes on this facet. Differentiation of the respiratory passages begins within the fetal stage and proceeds from distal to proximal alongside the branches of the respiratory diverticulum. Alveolar formation begins towards the end of the fetal interval and continues until the age of two to three years. The surrounding splanchnic mesoderm develops into the cartilage and fibrous connective tissue of the larger airways and the blood vessels and supporting tissues of the smaller airways and alveoli. Cranial to the foregut and caudal to the hindgut, the connection of embryonic construction to adult derivatives is much less obvious. For instance, the oral membrane, which is a fusion of ectoderm and endoderm, is the cranial boundary of the foregut (in the adult this boundary is at the stage of the tonsillar fauces). The oral cavity develops cranial to the oral membrane from an ectodermal depression, the stomodeum, bounded by the primary pharyngeal arch and the frontal course of.
Effective calcitriol 0.25 mcg
Integrin-dependent organization and bidirectional vesicular traffic at cytotoxic immune synapses. Natural killer cell lytic granule secretion happens by way of a pervasive actin network at the immune synapse. Remodelling of cortical actin where lytic granules dock at natural killer cell immune synapses revealed by super-resolution microscopy. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is tremendously impaired in perforin-deficient mice [see comments]. Spectrum of perforin gene mutations in familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Primary hemophagocytic syndromes point to a direct link between lymphocyte cytotoxicity and homeostasis. Severe and progressive encephalitis as a presenting manifestation of a novel missense perforin mutation and impaired cytolytic exercise. Perforin and granzymes have distinct roles in defensive immunity and immunopathology. Granzyme A is crucial for restoration of mice from an infection with the pure cytopathic viral pathogen, ectromelia. In vitro- and ex vivo-derived cytolytic leukocytes from granzyme A � B double knockout mice are defective in granule-mediated apoptosis however not lysis of target cells. The differential contribution of granzyme A and granzyme B in cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated apoptosis is decided by the standard of target cells. Functional dissociation of DeltaPsim and cytochrome c launch defines the contribution of mitochondria upstream of caspase activation throughout granzyme B-induced apoptosis. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-induced killing within the absence of granzymes A and B is unique and distinct from both apoptosis and perforin-dependent lysis. Mitochondria-dependent and -independent regulation of Granzyme B-induced apoptosis. A novel mechanism for protein supply: granzyme B undergoes electrostatic change from serglycin to goal cells. Cationic sites on granzyme B contribute to cytotoxicity by selling its uptake into goal cells. Granzyme B binds to goal cells mostly by charge and must be added concurrently perforin to set off apoptosis. A clathrin/dynamin- and mannose-6-phosphate receptor-independent pathway for granzyme B-induced cell dying. Adenovirus L4-100K meeting protein is a granzyme B substrate that potently inhibits granzyme B-mediated cell demise. A novel area in adenovirus L4-100K is required for stable binding and efficient inhibition of human granzyme B: potential interaction with a species-specific exosite. Functional dimension of complement and perforin pores in contrast by confocal laser scanning microscopy and fluorescence microphotolysis. Isolation and biochemical and useful characterization of perforin 1 from cytolytic T cell granules. Structural/functional similarity between proteins involved in complement- and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Protection from endogenous perforin: glycans and the C terminus regulate exocytic trafficking in cytotoxic lymphocytes. Perforin is activated by a proteolytic cleavage throughout biosynthesis which reveals a phospholipidbinding C2 area. Perforin prompts clathrin- and dynamin-dependent endocytosis, which is required for plasma membrane repair and supply of granzyme B for granzyme-mediated apoptosis. Large plasma membrane disruptions are quickly resealed by Ca2+-dependent vesicle-vesicle fusion events. Cytosolic delivery of granzyme B by bacterial toxins: evidence that endosomal disruption, in addition to transmembrane pore formation, is a crucial perform of perforin. Cell surface-bound warmth shock protein 70 (Hsp70) mediates perforin-independent apoptosis by specific binding and uptake of granzyme B. Granzyme B short-circuits the necessity for caspase eight exercise during granule-mediated cytotoxic T-lymphocyte killing by immediately cleaving Bid.
Discount 0.25 mcg calcitriol otc
In contrast, the transcription issue En1 is required for ventral limb patterning and eccrine gland formation. Hoxc13 is an important homeodomain-containing gene for later levels of follicular and nail differentiation, no less than in murine fashions. Candidates for prenatal testing include fetuses with an affected sibling or family member. The pores and skin is doughy, and patients have skeletal abnormalities and basic failure to thrive. Argininosuccinic aciduria is an autosomal recessive dysfunction, resulting from faulty argininosuccinate lyase; it might current neonatally with trichorrhexis nodosa and brief, damaged scalp hairs, neurologic deficits including lethargy and psychological retardation, hepatomegaly, and failure to thrive. Diseases similar to pachyonychia congenita current primarily with cutaneous and ectodermal appendageal defects, together with hyperkeratotic nails, palmoplantar keratoderma, follicular hyperkeratosis, and steatocystoma multiplex. These defects have been found to be mutations in typical "delicate" keratin genes: K6a, K6b, K16, and K17. Matsui T, Amagai M: Dissecting the formation, construction and barrier operate of the stratum corneum. Haniffa M, Gunawan M, Jardine L: Human skin dendritic cells in health and disease. Richard G, Choate K, Milstone L, et al: Management of ichthyosis and associated situations gene-based prognosis and rising gene-based remedy. Samuelov L, Sprecher E: Peeling off the genetics of atopic dermatitis-like congenital issues. Sheng J, Ruedl C, Karjalainen K: Most tissue-resident macrophages besides microglia are derived from fetal hematopoietic stem cells. Kamaraj B, Purohit R: Mutational analysis of oculocutaneous albinism: a compact evaluate. Kume T: Specification of arterial, venous, and lymphatic endothelial cells during embryonic development. Chen H, Griffin C, Xia L, et al: Molecular and mobile mechanisms of lymphatic vascular maturation. Bostwick B, Fang P, Patel A, et al: Phenotypic and molecular characterization of focal dermal hypoplasia in 18 people. Vanakker O, Callewaert B, Malfait F, et al: the genetics of sentimental connective tissue issues. Bruckner-Tuderman L, Has C: Disorders of the cutaneous basement membrane zone-the paradigm of epidermolysis bullosa. Lu C, Fuchs E: Sweat gland progenitors in development, homeostasis, and wound restore. The lung and gut are usually seen as change surfaces for gases and vitamins; the skin is more generally thought of a barrier. This protective position is clear at delivery because the fetus abruptly transitions from a heat, moist, sterile, protected sphere to a cold, dry, microbe-laden world full of bodily, chemical, and mechanical risks. Focusing only on the barrier properties of the pores and skin, nonetheless, minimizes the crucial position of the skin in social communication, notion, and behavioral interactions. The pores and skin, as the floor of an organism, is both a mobile and a molecular construction, in addition to a perceptual and psychological interface. Many vertebrates, similar to amphibians, reside on land however are confined to humid or moist microhabitats. Reptiles and fish have a skin floor lined predominantly with scales; birds have evolved feathers; and most mammals are coated with a protecting mantle of fur. Among primates, humans are unique in possessing a nonfurred skin with a thick stratified interfollicular dermis and a well-developed stratum corneum. The query of the presumptive advantage of losing a protective and insulating coat of fur has long intrigued evolutionary biologists and bodily anthropologists. The close embryologic connection between the epidermis and the brain (both are ectodermal derivatives) helps the rivalry that these peculiar structural elements of human development have coevolved. Cutaneous attributes type the basis for a lot of readily noticed biologic distinctions (age, race, sex), in addition to a number of, overlapping sociocultural traits (tattooing, cosmetics, tanning). During recovery from sickness, the skin varieties a important interface linking a affected person with caregivers and a nurturing setting. In this articler, particular elements of the physiologic development of fetal and neonatal pores and skin are highlighted, focusing notably on the event of the epidermal barrier and the capabilities subserved by the outermost layer of the skin, the stratum corneum. Where relevant, new areas of pores and skin biology pertinent to a fetus and a new child are emphasized.
Purchase genuine calcitriol
In these paired studies, four �g/kg/minute thirteen D-[U- C]glucose tracer was infused by prime constant infusion to decide Ra, during saline or glucose infusion, the latter at a rate of 5. In comparability with that through the saline infusion turnover period, the plasma glucose focus elevated significantly in the course of the glucose infusion turnover interval, from 88 � 3 to 101 � 4 mg/dL. Plasma insulin concentration remained unchanged (12 � 5 �U/mL versus 8 � three �U/mL). Of the 5 infants who showed decreased Ra during glucose infusion, three acquired glucose at a fee exceeding basal Ra. Of the remaining six infants who exhibited persistent Ra throughout glucose infusion, three acquired glucose at a rate equal to or in excess of basal Ra. These data suggested that glucose homeostasis in low-birth-weight infants is transitional all through the neonatal interval. It is feasible, as noted by Hetenyi and colleagues,36 that the decreased neonatal response to insulin and different hormones. Diminished responsiveness to each insulin and counterregulatory hormones ought to help in maintaining glucose homeostasis within the neonate. Other investigators, in more recent research, examined the hypothesis that the imprecise control of glucose manufacturing by insulin is mirrored by a corresponding lack of 10. In 30 spontaneously delivered time period lambs, glucose kinetics were measured after administration of radiolabeled isotope utilizing the primed constant infusion technique. The results suggested that insulin exerted a higher impact on glucose uptake than on glucose manufacturing. The imprecise effect of those counterregulatory hormones on neonatal glucose production mirrors the beforehand documented imprecise control by insulin. Complete suppression of glucose manufacturing was noticed within the adult group, whereas an 80% reduction was achieved within the newborn pet group. These employees attributed a scarcity of full suppression of glucose manufacturing in the neonate to hepatic resistance to insulin and chronic gluconeogenesis. Kahn52 defined insulin resistance and supplied a distinction between insulin insensitivity and insulin unresponsiveness. Insulin insensitivity is characterised by a shift to the best on the insulin dose-response curve such that the next concentration of insulin is critical to produce a half-maximal effect, with a maximal effect achieved ultimately. This shift often is the results of decreased affinity or a decreased focus of insulin receptors. With insulin unresponsiveness, all responses to insulin are lowered (including the maximal response), however the dose-response relationship remains normal. A combination of both forms of insulin resistance might exist simultaneously, so that the next insulin concentration would be required to produce a half-maximal effect, and the maximal impact could be decreased compared with that of a normal response. The euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp technique to examine in vivo insulin sensitivity and the hyperglycemic clamp technique to assess insulin secretion are being used to investigate a selection of conditions that includes evidence of insulin resistance. The % reduction in endogenous glucose production ranged from 41% to 58% of basal rates, and protracted glucose production. This sample of response to insulin is most according to a postreceptor defect. Decreased receptor concentration or affinity is an unlikely clarification, because at least in the human adult, loads of so-called spare insulin receptors can be found after the number of receptor websites required to obtain a maximal response are occupied. Even although that plateau was not finally reached at these insulin infusion charges, the neonatal glucose utilization response to insulin, even at a decrease plasma insulin focus, far exceeded that reported in the literature because the maximal response in the grownup. This specific issue is of present interest, but the limited amount of adipose tissue within the preterm neonate might probably intrude with the indirect impact of insulin on endogenous glucose production. As noted previously, Goldman and Hirata41 instructed that an attenuated response to insulin in the very-low-birth-weight neonate is the explanation for the occurrence of hyperglycemia. They attributed this response to insulin resistance, somewhat than lack of the beta cell response. In other research, by contrast, abrupt and sustained enchancment in glucose tolerance has been reported to happen in response to short-term and long-term insulin infusions. An approximate 50% discount in glucose manufacturing has been reported in response to an exogenous glucose infusion fee of approximately 4 to 6 mg/kg/minute. Hertz and associates noted a whole suppression of glucose production in steady, extraordinarily untimely infants when a high glucose infusion rate. The glucose load resulted in a major increase in each plasma glucose and insulin concentrations. At an analogous plasma insulin focus, a 41% reduction in glucose manufacturing was famous, so the mixed impact of glucose and insulin appears necessary for full suppression of glucose manufacturing.
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Calcitriol
Flint, 25 years: Vanderpas J, Vertongen F: Erythrocyte vitamin E is oxidized at a lower peroxide concentration in neonates than in adults. The inhibitory impact of C-reactive protein on bacterial phosphorylcholine platelet-activating factor receptor-mediated adherence is blocked by surfactant. The granzyme B inhibitor, protease inhibitor 9, is mainly expressed by dendritic cells and at immune-privileged sites. Cells of the epiblast turn out to be organized into an epithelial disk, the progenitor of all embryonic tissues, in addition to the extraembryonic mesoderm, amnion, and yolk sac.
Rakus, 53 years: Karbach U, Ewe K: Calcium and magnesium transport and affect of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Nagy A, Rossant J, Nagy R, et al: Derivation of fully cell culture-derived mice from early-passage embryonic stem cells. Hirata H, Bessho Y, Kokubu H, et al: Instability of Hes7 protein is essential for the somite segmentation clock. They have the power for sequence-independent dealing with of four hundred variable dipeptides and 8000 tripeptides.
Avogadro, 26 years: Reflections on the implications of multistage carcinogenesis for the nature of neoplasia. Meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae in infant rats: protecting immunity and antibody priming by gastrointestinal colonization with Escherichia coli. Most thiazide diuretics are thought of compatible with breastfeeding if doses are stored low. The speedy developmental change in physiology among neonates lends itself to analysis by Monte Carlo simulations to perceive the range of possible drug concentrations which are more likely to be produced when pharmacokinetic parameters change with maturation or organ dysfunction.
Trompok, 31 years: Reciprocal functional modulation of the activation of T lymphocytes and fibroblasts derived from human strong tumors. T cell traces that transfer protective immunity or exacerbation belong to totally different T helper subsets and respond to distinct parasite antigens. Suggestive evidence factors to a causal affiliation between severe maternal zinc deficiency resulting from acrodermatitis enteropathica and congenital malformations, together with neural tube defects. Human herpes virus 6 is the commonest organism, followed by human cytomegalovirus, parvovirus B19, and Epstein-Barr virus.
Garik, 40 years: Fas ligand mutation in a affected person with systemic lupus erythematosus and lymphoproliferative disease. Screening modalities embrace evaluate of the clinical history for each the patient and her partner, analysis of maternal serum markers or noninvasive prenatal screening results, and ultrasound examination in each the primary and second trimesters. It is due to this fact obvious that for substances with small extraction coefficients, accuracy in measuring umbilical uptake using the Fick precept is problematic. There was an early belief that they might be endlessly plastic inside their tissue of residence, capable of give rise to all cell sorts dictated solely by the environmental cues of a selected area and developmental epoch.
Gelford, 64 years: In two case stories, infants have suffered vital respiratory melancholy attributable to this metabolite. Parent-of-origin effects on the incidence of a genetic disease are a mirrored image of the phenomenon of imprinting. Nod2-dependent regulation of innate and adaptive immunity within the intestinal tract. Saturable magnesium absorption is low compared with the total magnesium-absorptive flux, indicating a modest mobile, regulated Mg2+ flux.
9 of 10 - Review by C. Grimboll
Votes: 300 votes
Total customer reviews: 300
References
- Jacobs DO. Clinical practice. Diverticulitis. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(20):2057-2066.
- Broadie TA, Glover JL, Bang N, et al. Clotting competence of intracavitary blood in trauma victims. Ann Emerg Med. 1981;10(3):127-130.
- Mizuguchi Y, Oishi Y, Miyoshi H, et al: The functional role of longitudinal, circumferential, and radial myocardial deformation for regulating the early impairment of left ventricular contraction and relaxation in patients with cardiovascular risk factors: A study with two-dimensional strain imaging, J Am Soc Echocardiogr 21:1138-1144, 2008.
- Hensle TW, Bingham JB, Reiley EA, et al: The urological care and outcome of pregnancy after urinary tract reconstruction, BJU Int 93(4):588-590, 2004.
- Svensjo S, Bengtsson H, Bergqvist D: Thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm and dissection: an investigation based on autopsy, Br J Surg 83(1):68-71, 1996.
- Heusch G:-Adrenergic mechanisms in myocardial ischemia, Circulation 81:1, 1990.
- Fukui M. Current state of study on moyamoya disease in Japan. Surg Neurol 1997;47(2):138-43.


