Christopher M. Bland, PharmD, BCPS, FIDSA
- Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Clinical and Administrative Pharmacy, University of Georgia College of Pharmacy
- Critical Care/Infectious Diseases Clinical Pharmacist, St. Joseph�s/Candler Health System, Savannah, Georgia

https://rx.uga.edu/faculty-member/christopher-m-bland-pharm-d/
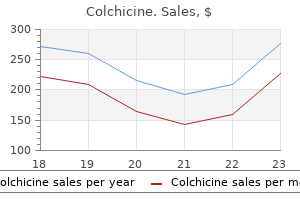
Colchicine dosages: 0.5 mg
Colchicine packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Purchase colchicine 0.5mg line
Blast Brachy Brady Cry Crypt(o) Cyt Fibr Gyn Hetero Hydr Leio Lith Micr Morph Myc Neo 011g Onc Pachy Pan Pseudo Py Sciirh Scoho Meaning Unequal Imperfect Germobe Short Slow Cold Hidden Cell Ropelike Woman Different Water Smooth Stone Small Form Fungus New Few Tumour Thick All False Pus Hard Crooked. Example Anisocytosis Atelectasis Blastomycosis Brachygnathia Bradyeardia Cryosurgery Cryptorchidism Cytology Fibroma Gynaecology Heterogeneous Hydronephrosis Leiomyoma Cholelithiasis Microscope Morphology Mycoplasm Neoplasm Oliguiia Oncology Pachyderm Pan hysterectomy Pseudocyesis Pyorrhoea Scirrhous Scoliosis Meaning of example Medical Terminology Course 89 Prefix Sten Tachy Toxi Troph Vas Suffixes Suffix orna algia atresia blast cele dde cleisis clysis cyst cyte dynia ectasis emesis Meaning Contracted Fast Poison Example Stenosis Tachycardia Meaning of instance Toxicology Thyrotropic Nourishmen4Vasospasm Vessel Meaning New growth Pain Without opening Germ Swelling Killer Closure Injection Sac of fluid Cell Pain Expansion Vomiting Example Carcinoma Neuralgia Proctatresia Myeloblast Hydrocele Germicide Enterocleisis Hypodermoclysis Dacrocyst Leukocyte Pleurodynia Atelectasis Haematernesis Meaning of Example Suffix aemia iris lith ogy malacia orexia pathy penia plasia pnoea ptosis orrhagia rrhoea spasm stasis uria Example Meaning Anaemia Blood Inflammation Iritis Fecolith Stone Biology Study of Osteomalacia Softening Anorexia Appetite Adenopathy Disease Thrombopenia Poor Aplasia Formation Dyspnoea Breathing Nephroptosis A falling Bursting forth Metrorrhagia Diarrhoea Flow Pylorospasm Contraction Metastasis Position In the urine I Haematuria Meaning of example. Appendices, discovered on the finish of the textual content, present medical abbreviations, word components and their meanings, and answers to self-check questions. Following the appendices are a bibliography and picture credits, as nicely as an index. The classes emphasize the essential material discussed in the textual content and supply additional ideas or examples to help you grasp the material. Note the chapters for each assignment in the textbook and browse the project in the textbook to get a general concept of its content. Study the assignment, taking note of all particulars, particularly the primary concepts. After answering the advised questions, verify your answers with these given in the again of the study guide. If you miss any questions, evaluation the pages of the textbook masking those questions. These numbers are for reference solely in case you have reason to contact Student Services. A compound word may encompass two word roots, such as in the case of collarbone (collar + bone). To facilitate the pronunciation of phrases, a combining vowel is placed in between word roots. Aprefix is hooked up earlier than the word, while a suffix is placed on the finish of a word root. Guidelines Linking combining varieties Linking combining formsandsuffixes Linking combining formsandsuffixes with initial vowels Linking different word partsandprefixes In most situations, the combining vowel is retained amid combining forms. For occasion, appendectomy may be written as append + ectomy to highlight its component elements. Note: Abbreviations and symbols should be used cautiously, particularly when medicines are involved. The department of science that offers with the preparation, properties, makes use of, and actions of drugs is identified as pharmacology. Drugs, mostly referred to as medicines, are used within the prevention and treatment of ailments. The suffix-istmeans"onewho";therefore,ananesthetist is one who administers anesthesia. An anesthetist could be a doctor or a nurse, whereas an anesthesiologist is a medical physician orphysician. Polypectomy and adrenalectomy refer to the excision or elimination of polyps and adrenal glands, respectively. Colonoscopy is a method of visualizing thecolonwiththeuseofafiber-optic instrument. Colostomy is a surgical procedure that creates a gap for the colon or giant intestine via the stomach. Encephalopathy is a general time period that refers to a dysfunction or disease of the mind. Osteoporosis is a disease that weakens the bones, thereby increasing the risk for fractures. Asymptom signifies a disorder or illness in which adjustments in health standing are perceived by the client. Omphalocele is an stomach wall defect by which the abdominal organs protrude by way of a gap on the base of the umbilical cord. Angioedema involves the precipitous swelling of the tissues underneath the skin, often due to an allergic response. Lymphoma refers to a group of blood cancers originating from the lymphatic system. Neutropenia refers to abnormally low levels of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell. The word microscope (word part= micro), for example, is used not solely by healthcare professionals but in customary language as well. A 78-year-old man who had a blood vessel removed throughout surgical procedure is more likely to have which time period documented in his chart During a bodily examination, a physician can visualize the eardrum utilizing a device known as an a.
Order generic colchicine on line
The left atrium is the posterior surface of the heart while the left ventricle comprises the diaphragmatic floor. The superior aspect of the anterior surface of the heart is notable for a visualization of the origins of the great vessels: superior vena cava, aorta, and pulmonary trunk. The superior facet of the posterior surface, the left atrium, is notable for the visualization of the 4 pulmonary veins. The orientation of the chambers can be further achieved by following the sulci or grooves shaped from fusion of the muscular partitions during improvement. The coronary sulcus is the groove separating the atriums from ventricles and could be seen in slide 6 running between the proper auricle and the proper fringe of the pulmonary trunk. The anterior interventricular sulcus is the groove separating the ventricles on the anterior floor while the posterior interventricular sulcus separates the ventricles on the diaphragmatic floor. This slide exhibits the anterior and posterior views of the great veins as they enter the guts. The venous move from the decrease limbs, stomach, and pelvis returns through the inferior vena cava and enters the best atrium. Newly oxygenated blood returns to the left atrium via the proper and left superior and inferior pulmonary veins. These veins are distinctive in that they carry oxygenated blood in contrast to different adult veins. This slide reveals the anterior and posterior views of the great arteries of the center. The deoxygenated blood leaves the heart and travels to the lungs by way of the pulmonary trunk and the right and left pulmonary arteries. The blood is returned to the systemic circulation through the aorta arch which gives rise to the brachiocephalic trunk, the left frequent carotid artery, and left subclavian artery. The brachiocephalic trunk supplies blood to the proper upper limb and head via the right subclavian artery and right common carotid artery respectively. The left widespread carotid artery then provides the left head and neck whereas the left subclavian artery provides the left upper limb. The pericardium is a fibroserous sac containing the guts and the origins of the great vessels. It is made up of an outer wall and an inside wall separated by a pericardial cavity. The outer wall consists of an outer connective tissue layer known as fibrous pericardium fused with an inside serous layer known as the parietal layer of serous pericardium. Serous tissue simply refers to a skinny membrane lining a closed physique cavity moistened with serous fluid. The closed body cavity on this case is the pericardial cavity separating the 2 fused outer wall layers with the inside wall known as the visceral layer of serous pericardium. The parietal and visceral layers of serous pericardium meet and are steady at the origins of the nice vessels forming reflections. The reflections (meeting of the parietal and visceral pericardium) occurring on the aorta and pulmonary trunk form the transverse sinus. When the pericardium is opened anteriorly or with the guts removed a finger may be positioned within the transverse sinus to separate the aorta and pulmonary artery from the superior vena cava. With a bit of the pericardial sac removed, the relationships off the posterior surface of the heart (left atrium) can be visualized. The descending aorta, additionally referred to as the thoracic aorta, has a easy shiny reddish shade and is found traveling just left of the muscular appearing esophagus. The left vagus nerve can be seen touring with the descending aorta earlier than it moves anterior to the esophagus to turn into the anterior vagal trunk. The meshwork of small nerves overlaying the esophagus is the esophageal nerve plexus. Note that this slide also allows a visible distinction between the fused outer fibrous pericardium in white with the internal parietal layer of serous pericardium in tan. Showed here are the diaphragmatic relationships of the guts at the T8/T9 vertebral degree. Several constructions cross by way of the diaphragm including the inferior vena cava as it returns blood from the liver and hepatic veins. To the proper of the descending aorta is the thoracic duct permitting lymphatic drainage.
Diseases
- Glycogen storage disease type 9
- Perniosis
- Familial multiple trichodiscomas
- Hypertryptophanemia
- Fronto-facio-nasal dysplasia
- Paraomphalocele
0.5 mg colchicine mastercard
As K+ conductance through inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) channels decreases, and Na+ and Ca2+ conductance increases, spontaneous depolarization during part four happens. Phase zero has a a lot decrease slope in pacemaker cells, where the major membrane occasion governing depolarization in phase zero is Ca2+ inflow via slow channels. As indicated, the faster part 0 depolarization of the myocardium and Purkinje fibers is triggered primarily by the Na+ influx through fast channels. Differential effects on these ion fluxes help clarify variations within the therapeutic makes use of and opposed results of the antiarrhythmic medication. Each present and its corresponding channel are defined by the rapidity with which they activate. The advanced interplay of ionic currents that represent the cardiac motion potential is based on the power of ion channels to sense and reply to variations within the membrane potential. Channels which might be in a closed resting state open when a specific threshold potential is reached. The induced depolarizations may be early (before repolarization is complete) or delayed (after full repolarization has occurred), however each can end result in sustained tachyarrhythmias. As illustrated, conduction in one department is normal, whereas impulses in a second department can proceed in only the reverse path (unidirectional block). A normally performed impulse via department 1 could be conducted in retrograde style by way of branch 2 to re-excite an area of tissue that was previously excited by the traditional path of conduction. For this "circadian movement" to occur, the tissue in path 1 must have repolarized to a point at which excitation is feasible (which often implies that the retrograde conduction is relatively slow). A wave of re-excitation touring in a round path via fiber 1, the contractile cardiac muscle, and fiber 2 can lead to a self-sustaining arrhythmia. Reentry is usually a serious contributor to atrial fibrillation, an arrhythmia particularly frequent in elderly people. Disturbances in the relationship of the fast and sluggish electrical responses of certain cardiac cells may play an important role within the genesis of arrhythmias. The fast response refers to the speedy phase 0 depolarization caused by rapid Na+ influx. This type of exercise is seen in atrial and ventricular muscle fibers and specialized conducting fibers. In addition to the rapid inward present carried by Na+, the quick fibers exhibit a second, slower inward present carried by Ca2+. In B, "unidirectional block" signifies an space of damage that blocks normal electrical flow however allows the impulse to find its method again against the move where it could set off one other unintended cycle. Most ion channels spontaneously shut, or become inactivated, over a attribute timeframe, and the ion flux abruptly decreases. Channels within the inactivated state are unresponsive, or refractory, to the original stimulus and remain so until the membrane potential returns to a value that permits the channels to assume once more a ready-to-open conformation. As discussed in subsequent sections of this chapter, many antiarrhythmic medication bind preferentially to specific conformations of ion channels and exert differing results on the action potential. Arrhythmias are thought to originate from irregular impulse era, impulse conduction, or both in combination. Some arrhythmias attributable to irregular impulse technology end result from elevated automaticity. These tachyarrhythmias are often in response to an increase within the rate of diastolic depolarization (increased slope of section 4) in pacemaker cells. Phase 4 depolarization can be altered by autonomic nervous system activity, by hormones, or by drugs. In current years, a remarkable variety of cardiac medicines have been launched to the market that have truly allowed better survival and high quality of life for many who are diagnosed in time. In Chapter 20, the drugs utilized in coronary heart failure are covered, and in Chapter 21 the drugs used for angina are mentioned. Of course, correct cardiac care often includes other classifications of medication such as anticoagulants, diuretics, pulmonary medications, and others. In all arrhythmias, some aspect of the conventional electrophysiologic system that governs cardiac contraction is behaving abnormally. Nonpharmacologic interventions for cardiac arrhythmias include electrical cardioversion, automatic implantable cardioversion/defibrillation units, ablation therapy, and pacemakers.
Buy 0.5mg colchicine free shipping
In some circumstances, heel lifts assist; occasionally, if the pain is extreme, a under knee strolling cast is required. Any underlying deformity or foot kind with abnormal operate should be assessed and treated. Plantar fascia affections Pain alongside the medial longitudinal arch is sort of common. Little evidence supports ultrasound remedy, local steroid injections or shortwave diathermy. It is typically seen in aged people as their fats pads atrophy or in those who abruptly turn into more lively. Clinical features-A generalized warm, dull throbbing pain is felt over the weight-bearing area of the heel; this develops over a number of months. Ultrasound therapy and shortwave diathermy are sometimes used, but controlled trials are few. Rheumatoid nodules, and infrequently gouty tophi, can be discovered inside the substance of the Achilles tendon. Increased exercise resulting in an overuse syndrome could also be a feature in younger, lively sufferers. Partial or complete ruptures of the tendon need immobilization and surgical restore. For inflammatory situations, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may assist, as might ultrasound therapy, friction, relaxation and shock-absorbing heel lifts. Inflammation could additionally be triggered by overuse via poor foot mechanics; in such instances, orthoses might management the pronation. Achilles tendon affections Inflammation of the Achilles tendon and surrounding delicate tissue may be related to overuse or systemic inflammatory problems (Box 7. Inflammation of the tendon, peritendon tissues and bursae give slightly different clinical photos. Conditions similar to xanthoma can even have an effect on the Achilles tendon and produce fusiform swelling within the tendon. In such circumstances, ldl cholesterol concentrations Pain in the Foot 43 Arthropathies that affect the foot Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis in the foot may be asymptomatic, but it could possibly lead to ache, joint stiffness, practical loss and incapacity. The most common websites are the primary metatarsophalangeal joint (hallux rigidus) and the tarsus joints. Biomechanical elements are sometimes involved in the development of degenerative joint changes (for example, compensatory foot pronation in subtalar osteoarthritis). Trauma, recurrent urate gout, and the demands of fashion-such as inappropriate footwear-are different factors; nevertheless, the broad fashion of modern sneakers may be helpful. Rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatoid arthritis typically starts within the foot, particularly on the metatarsophalangeal joints. The forefoot is painful and stiff, and direct transverse pressure to the forefoot or squeezing a single metatarsophalangeal joint is painful. In the early phases of the disease, the hind foot, notably the subtalar joint, may also be painful. In persistent rheumatoid feet, severe pain within the forefoot might continue, with a sensation of walking on pebbles. In radiographs, inflammatory spurs may be seen on the calcaneum on the insertion factors of the Achilles tendon and plantar fascia. Painful stiff interphalangeal and metatarsophalangeal joints, usually in an asymmetrical sample, are frequent. Nail dystrophy could also be seen, with typical psoriatic pitting, onycholysis, subungual hyperkeratosis, discoloration and transverse ridging. Pustular psoriasis and keratoderma blennorrhagica on the plantar aspect of the foot might contribute to ache when strolling. The diabetic foot-In the presence of neuropathy, the diabetic foot is weak to developing an acute progressive Charcot-like arthropathy. Patients complain of (paradoxically) ache and swelling within the foot, often after minor trauma. Untreated it will rapidly deteriorate, leaving a disorganized and dysfunctional foot.
Discount colchicine online
Stimuli from various sources, and of various varieties, are obtained and become the electrochemical signals of the nervous system. Sensation is the activation of sensory receptor cells at the level of the stimulus. Sensation involves receptors which are the cells or structures that directly work together with the bodily stimulus resulting in a change in the receptor cell. That change will stimulate a series of sensory neurons which transmit the data to sensory cortices in the cerebrum the place that info is integrated. Integration of data in the sensory cortices offers meaning to the sensory stimuli and supplies a aware interpretation of that stimulus, known as perception. Notably, perception relies on sensation, however not all sensations are perceived. The fundamental rules of sensation and perception apply to all forms of sensory stimuli we interact with including contact, taste, smell, hearing, equilibrium, and vision. The main structure associated with imaginative and prescient is the eyeball however there are additionally a quantity of accent structures which might be crucial for our capability to see the world around us. The bony orbit surrounds the eyeball, protecting it and serving as an anchor for delicate tissues that help the eyeball. Eyelids, with lashes at their leading edges, help to protect the attention from abrasions by blocking particles which will land on the floor of the eye. The inner floor of every eyelid accommodates a skinny membrane called the palpebral conjunctiva which is continuous with the ocular conjunctiva which extends over the white areas of the eye, connecting the eyelids to the eyeball. The manufacturing of tears by the lacrimal gland washes the floor of the eyeball to forestall the buildup of overseas material and nourish the cells of the cornea. The lacrimal gland, discovered in the superolateral portion of the orbit, releases fluid via lacrimal ducts onto the surface of the eye the place the fluid flows to the medial nook of the attention and is collected via the lacrimal punctum. The collected fluid strikes via the lacrimal canaliculus, into the lacrimal sac, by way of the nasolacrimal duct, into the back of the nasal cavity, and down into the throat. Four of the muscular tissues are arranged on the cardinal points across the eye and are named for those places. When every of these muscle tissue contract, the eye to moves toward the contracting muscle. The superior indirect originates at the posterior orbit, close to the origin of the four rectus muscle tissue. However, the tendon of the indirect muscular tissues thread through a pulley-like piece of cartilage generally known as the trochlea. The angle of the tendon through the trochlea implies that contraction of the superior indirect rotates the attention medially. The inferior indirect muscle originates from the ground of the orbit and inserts into the inferolateral surface of the eye. When it contracts, it laterally rotates the attention, in opposition to the superior oblique. When the attention seems up or down, the eye must additionally rotate slightly to compensate for the superior rectus pulling at approximately a 20-degree angle, rather than straight up. The similar is true for the inferior rectus, which is compensated by contraction of the inferior oblique. The lateral rectus, which causes lateral movement of the attention, is innervated by the abducens nerve. The motor nuclei of these cranial nerves all hook up with the mind stem which coordinates eye movements. The outermost layer is the fibrous tunic, which includes the white sclera and clear cornea. The center layer of the attention is the vascular tunic, composed of, from posterior to anterior, the choroid, ciliary body, and iris. The choroid is a layer of extremely vascularized connective tissue that provides a blood provide to the opposite layers of the eyeball. Anterior to the choroid is the ciliary physique, a muscular construction that attaches to the lens by suspensory ligaments. The ciliary physique and suspensory ligaments change the form of the lens, permitting it to focus mild onto specific areas in the again of the attention. Overlaying the ciliary physique, and visible in the anterior eye, is the iris-the coloured a half of the eye.
Discount colchicine 0.5 mg on line
The lateral or fibular collateral ligament joins the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the head of the fibula. The medial or tibial collateral ligament joins the medial epicondyle of the femur to the lateral facet of the proximal tibia. The medial collateral ligament is more vulnerable to harm than is the lateral collateral ligament, as a end result of its vulnerability when a drive pushes into the lateral aspect of the knee. This ligament runs from the patella to the tibial tuberosity and is a portion of the quadriceps tendon of insertion. The patellar ligament provides extra stability across the anterior side of the knee joint. The articulating surfaces of the sacrum and ilium nestle towards each other, so that the joints permit very little movement. Hip Joint the hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint designed to have the soundness wanted for a weight-bearing joint. A sturdy ring of fibrocartilage, known as the acetabular labrum, connects to the sting of the acetabulum, giving the socket higher depth and serving to to hold the head of the femur in the socket. The ischiofemoral ligament, the iliofemoral ligament, and the pubofemoral ligament be a part of every of the hip bones to the femur. In addition, the ligament of the top of the femur joins the head of the femur to the acetabulum. The ischial bursa prevents friction between the gluteus maximus muscle and the ischial tuberosity. Pubofemoral ligament the iliolumbar ligament is part of a complex network of ligaments that stabilize the pelvic girdle and its connection to the lumbar spine. The inguinal ligament is the inferior margin of the aponeurosis of the external oblique muscle and superior border of the femoral triangle. The iliofemoral ligament, shaped like an inverted "Y", helps preserve optimum contact between the femoral head and acetabulum, limiting medial rotation and extension of the hip. Anterior sacrococcygeal ligament Obturator membrane Pubic symphysis A the posterior sacroiliac ligaments surround and stabilize the sacrum. They are part of a giant community of thick, strong ligaments situated within the pelvic area. Iliolumbar ligament Sacrospinous ligament Iliofemoral ligament the sacrotuberous ligament stabilizes the sacrum inferiorly and offers muscle attachment factors on the posterior pelvis. The ishiofemoral ligament spirals across the posterior coxal joint and assists the iliofemoral ligament in limiting medial rotation of the hip. Posterior sacrococcygeal ligaments anchor and stabilize the small, delicate coccyx. The lateral meniscus is circular formed cartilage that cushions the tibiofemoral joint and will increase joint continuity. The lateral collateral ligament connects the lateral femoral condyle to the head of the fibula. It is usually called the patellar ligament as a result of it connects the patella to the tibia. Proximal tibiofibular ligament Fibula Tibia Patella the posterior cruciate ligament connects posteriorly to the tibia and anteriorly to the medial condyle of the femur. Stronger than the anterior cruciate ligament, it prevents the tibia from sliding posteriorly and the femur from sliding anteriorly. The anterior cruciate ligament connects anteriorly to the tibia and posteriorly to the lateral condyle of the femur. It prevents the tibia from sliding anteriorly and the femur from sliding posteriorly. Femur the medial meniscus is a crescentshaped cartilage that cushions the tibiofemoral joint. A the posterior meniscofemoral ligament joins the lateral meniscus and the medial condyle of the femur. Patella the medial meniscus is a crescent-shaped cartilage that cushions the tibiofemoral joint. The lateral meniscus types an almost complete ring, whereas the medial meniscus is extra Cshaped. Several bursae help to forestall friction between constructions close to the knee joint.
Stinking Arrach (Arrach). Colchicine.
- Dosing considerations for Arrach.
- How does Arrach work?
- What is Arrach?
- Menstrual cramps and triggering menstrual flow.
- Are there safety concerns?
- Are there any interactions with medications?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96081
Order colchicine 0.5 mg with amex
However, incorporating as many elements of an optimally environment friendly movement technique as attainable, particularly facilitation of selective extension, maximises potential for recovery. Efficiency and independence in transfers may cut back secondary complications corresponding to hemiplegic shoulder pain, which has been proven to be extra 96 Moving Between Sitting and Standing prevalent in patients needing assist to switch (Wanklyn et al. These principles should be considered in transfers both with and without assistive units. Appropriate placement of the palms to a supporting surface can be used positively in remedy to: provide sturdy sensory info to assist orientate the patient in house. The alignment of the upper limbs could be facilitatory to , or interfere with, the activity and their use to provide orientation and stability quite than weight bearing is desirable. A vary of equipment is available to facilitate protected shifting and dealing with of sufferers which can also be used therapeutically at the aspect of cautious assessment, clinical reasoning and intervention for optimum carry-over. He was making attempts at this level to pull himself into standing with a standing help. His trunk alignment was poor, tending to fall backwards and to the left which in part associated to the burden of a very inactive left higher limb. This was exacerbated by the peak of the footrests which increased hip flexion and posterior pelvic tilt, although trunk asymmetry persisted, even when his feet had been on the floor. Any attempts to change his orientation away from 99 Bobath Concept: Theory and Clinical Practice in Neurological Rehabilitation the fall to the left side were met by resistance from fixation into aspect flexion of the right side of his trunk. Initial assessment additionally showed that his ability to organise his postural orientation and assist himself in standing was dominated by proper upper limb fixation and an inability to acquire midline and head orientation without help. He appeared to have a predominant presentation of impairment of the postural management techniques (see Chapter 2) and poor distal interplay of his hand to the plinth further impeding his postural orientation. His limited consciousness and integration of the left aspect of the physique into his body schema resulted in inadequate feed-forward control to create a more acceptable postural set for movements within and from the chair. Afferent data to his nervous system is dominated by stereotypical sensory data from his lively proper side however comparatively little information from the inactive left aspect. Feed-forward postural control to physique parts which have a poor illustration within the physique schema can be tough and so it can be hypothesised that by altering his orientation to the left and enhancing integration between the 2 sides, there can be a optimistic influence on his midline orientation. Initial treatment hypotheses: Integration of afferent info from each side would improve as fixation from the best is reduced and exercise on the left increased. Compensatory strategies being used in the ward situation will cut back if workers are guided to present appropriate assistance to each side of his body until enough postural management is acquired. This enabled evaluation of potential to facilitate improved left scapulothoracic alignment in preparation for involving the left upper limb in inserting for improved trunkal orientation. Pillow help was offered behind the trunk to help maintain extension as he grew to become extra appropriately postured. Head orientation to the proper facet is seen as a compensatory strategy, and this continued malalignment could result in restriction of vary and interfere with interpretation of vestibular data from the cervical afferents. Improvement in scapula setting on the left enabled increased weight transfer to the proper facet and reduction within the compensatory flexion. Having improved orientation to the right side, it was now possible to begin to acquire extra interaction between the 2 sides. Hypothesis refinement the positive response to reducing his fixation strategy in the right aspect and orientation to the left hand improved his postural symmetry. Further activation of his right upper limb would permit energetic weight switch in course of his proper facet without flexion and so enhance preparation to stand. Moving a limb away from the body requires each preparatory and accompanying postural activity, a perform of the reticulospinal pathways (Schepens & Drew 2006). Consequently, actions of the proper higher limb demand preparatory postural activation bilaterally but notably in the left side of trunk. Clinical experience has proven that sensory stimulation of the foot for improved segmental interaction with the ground can enhance activation within the limb to create standing. With direct facilitation of gastrocnemius, soleus has a reference from which to lengthen. Gaining heel contact with an applicable stretch of soleus creates a strong proprioceptive drive for the propulsion into standing. Maintenance of the size of the quadriceps additionally creates a drive to heel contact for initiation of standing exercise. As he achieved standing, his management was further facilitated by modification of the adduction technique in the best hip, combined with activation of left hip extension 106 Moving Between Sitting and Standing. His standing stability improved to the point the place he could free his head and preserve stability.
Purchase colchicine us
A clear description of the kinematics of stance phase has been offered by Moseley et al. For most of stance part, the hip is in extension requiring full eccentric management and length of the hip flexors. Hip extension and ankle dorsiflexion transport the vertical trunk phase from behind to in entrance of the stance foot, and speedy ankle plantarflexion at the end of stance further propels the physique forward. Early in stance the trunk is displaced laterally, accompanied by adduction 122 the Control of Locomotion on the stance hip and eversion of the stance foot (lateral pelvic displacement), so that the centre of mass is moved to a degree practically over the stance foot throughout the only assist section. The knee stays relatively prolonged all through the single assist part but flexes a small quantity in early stance. During the ultimate part of stance, the knee flexes in preparation for swing (Moseley et al. Swing section begins at toe-off and ends at heel strike because the foot is moved forward to a degree in entrance of the hips (Moore et al. During swing, the lower limb shortens adequately to permit the swinging foot to clear the bottom. Hip and knee flexion is followed by knee flexion to knee extension and dorsiflexion. The knee begins to flex within the last third of stance and continues flexing for the primary quarter of swing. Thereafter, the knee extends till just earlier than heel strike when slight flexion happens in preparation for the following stance phase. The hip begins to flex in the later a half of stance and completes flexion in the first half of swing. Ankle dorsiflexion begins simply after toe-off and peak dorsiflexion is reached by mid-swing and maintained all through the remainder of the swing phase (Moore et al. Mr S the foot is a key source of peripheral enter to control and modify the muscle activation pattern of the lower limb, notably during stance phase. The intrinsic muscular tissues within the foot are essential for the sufficient performance of ground reaction forces and the event of the appropriate kinetic chain of muscle activation to create sufficient stance for adequate swing. The drive platform allows the evaluation of the total pressure utilized by the foot to the bottom (Winter 1995). In quiet stance, the pressure is evenly distributed and the centre of pressure is positioned posterior to the ankle, halfway between the two ft. The ground response forces become very completely different when trunk accelerations are modified. A robust response with the bottom by way of heel contact is a vital part of producing environment friendly ground reaction forces and muscle activation patterns. Adequate heel contact with the bottom is a serious point of stability for ankle motion, and due to this fact selective dorsiflexion and plantarflexion. Stable heel contact with the bottom is also important for selective knee and hip motion in midstance. The single limb support phase is fundamental for producing and build up the kinetic power for the following swing. Clinical statement means that the stronger and longer the stance phase, the better the swing. Damage to the corticospinal system can produce long-term loss of the activation of the intrinsic musculature of the foot, which is important to create the postural stability for selective flexion and extension of the toes. Clinical statement suggests that the power to prolong the toes contributes to selective dorsiflexion as does the postural activity of abductor digiti minimi. Abductor digiti minimi is a key element of movement control of the foot because it helps the load of the lateral border and contributes to the comparatively weak peronei everting the foot, which is important for floor clearance and step initiation. Loss of size and energy in soleus as an antagonist will also considerably contribute to poor dorsiflexion of the foot. Unopposed dorsiflexion with out eversion often turns into inversion because of unopposed activity in tibialis anterior, especially when driven cortically.
Cheap 0.5 mg colchicine with visa
You can feel the temporalis move by putting your fingers to your temple as you chew. Additionally, the buccinator flattens the cheek space to maintain the cheek to the enamel so as to maintain food in the right place while chewing and in addition permits you to whistle, blow, and suck. Muscles of the anterior neck that insert on the hyoid bone are categorized according to their place relative to the hyoid bone, which is a small horseshoe-shaped bone positioned in the anterior midline of the neck. The digastric muscle has anterior and posterior bellies joined by an intermediate tendon situated on the hyoid bone that work to elevate the hyoid bone when you swallow. The mylohyoid muscle runs from the mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the ground of the oral cavity and depressing the tongue to the top of the mouth. The strap-like omohyoid muscle has a superior and inferior belly joined by a tendon which lies deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The head, connected to the top of the vertebral column, is balanced, moved, and rotated by a number of neck muscular tissues. The main muscle that laterally flexes and rotates the head is the sternocleidomastoid. Place your fingers on each side of the neck and switch your head to the left and to the best. It serves to pull down the mandible, open the mouth, and pull down the corners of the mouth, forming a frown. As an individual ages, the tissue connecting the platysma muscle tissue to the overlying skin loses its elasticity contributing to wrinkles and sagging in the neck. To correct this, a beauty surgical procedure called a platysmaplasty (commonly called a neck lift) can be carried out, which sutures the two platysma together. The scalene muscles work together to flex the neck, tilt and rotate the head, and also contribute to deep inhalation. The scalene muscular tissues embody the anterior scalene muscle (anterior to the center scalene), the medial (or middle) scalene muscle (the longest, intermediate between the anterior and posterior scalenes), and the posterior scalene muscle (the smallest, posterior to the center scalene). Additionally, the levator scapulae, as its name suggests, functions primarily is to elevate the scapula. The again muscles stabilize and move the vertebral column, and are grouped based on the lengths and course of the fascicles. The erector spinae group types the overwhelming majority of the muscle mass of the again and is the first extensor of the vertebral column. It controls flexion, lateral flexion, and rotation of the vertebral column, and maintains the lumbar curve. The girdle creates a base from which the head of the humerus, in its ball-and-socket joint with the glenoid fossa of the scapula, can transfer the arm in multiple instructions which was described intimately throughout Module three. Anteriorly positioned, the serratus anterior and pectoralis minor muscular tissues connect the ribs to the scapula while the trapezius, rhomboid main and rhomboid minor connect the scapula to the vertebral column on the posterior. The rhomboids are situated deep to the trapezius and when contracted, strikes your scapula medially, pulling the shoulder and upper limb posteriorly. Additionally, the pectoralis main and latissimus dorsi connect the trunk directly to the humerus on the anterior and posterior, respectively, permitting these massive muscle tissue to transfer the arm. Alternately, whenever you exhale, your chest falls because the thoracic cavity decreases in dimension. There are three sets of muscular tissues, called intercostal muscular tissues, which span each of the intercostal spaces. The eleven pairs of superficial exterior intercostal muscles help in inspiration of air throughout breathing because after they contract, they increase the rib cage, which expands it. Lying slightly below the externals, the eleven pairs of internal intercostal muscular tissues are used for expiration because they draw the ribs collectively to constrict the rib cage. Each external and inside intercostal muscle extends around the entire rib cage, with the inner intercostal all the time mendacity deep to the external intercostal. The third layer, the innermost intercostals, doubtless serve a similar position as the interior intercostals. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that allows a person to breathe by way of respiration.
Purchase line colchicine
Examples (b) (c) Medical Terminology Course iR (d) (e) embrace: penicillin, streptomycin, erythromycin, the tetracyclines and ampidillin. Pharmacodynarnic drugs serve either to depress specific body functions or to stimulate them. The tables that follow listing medicine generally used for various conditions of different body systems. Narcotic analgesics Comment Used to counteract despair Given for reduction of pain with out loss of consciousness Habit-forming analgesics Examples Amphetamines Morphine, Codeine, Demerol Darvon 2. Analgesic-antipyretics Hypnotics and sedatives In addition to pain-relieving this group reduces fever Exert a depressant effect on the nervous system. Can produce dependancy Phenobarbital, secobarbital, pentobarbital Paraldehyde, chloral hydrate Reserpine, Thorazine Meprobamate 1. Local Do not produce stupor even in massive doses Produces lack of sensation, accom- Nitrous oxide, cyclopropane panied by lack of consciousness Used as an adjunct to inhalation Sodium pentothal anaesthesia or alone for minor procedures Novocain, xylocaine Medical Terminology Course Table 9. Drugs that affect the respiratory system Category Antitussives Expectorants Comment Given to relieve cough Examples Codeine Aid in the expulsion of sputum Potassium iodine Table 11. Drugs that have an result on the gastrointestinal system Category Antacids Antiemetics Cathartics Antidiarrheals Antispasmodics Comment Counteract the acidity of the gastric contents Stops vomiting and relieves nausea Aid within the production of a bowel movement Cause discount in bowel actions Relieves spasms of the digestive tract Examples Amphojel, Gelusil Compazine, Dramamine Milk of Magnesia, Castor Oil, Cascara Sagrada Paregoric Lomotil Table 12. Drugs that have an effect on the circulatory system Category Cardiotonics Comment Improves the tone of myocardium Examples Digoxin Diuril Adrenalin Diuretics Vasoconstrictors Vasodilators Anticoagulants Increase the flow of urine Increase the tone of blood yessels Dilate the blood vessels Inhibit blood dotting Nitroglycerin, apresoLine Heparin, dicumarol Medical Terminology Course forty seven Table thirteen. Pharmaceutic abbreviations Name Ampules Capsules Compound Elixir Emulsion Enteric-coated Extract Fluid extract Liniment Liquid Lotion Mixture Abbreviation Amp. Many hospitals require their pharmacies to label all medicines with their generic name. The trade or model name is the special name given to a drug by each company manufacturing it. Causes of disease often fail underneath one of two basic headings: Predisposing causes; 2. Injury could also be produced by trauma, international bodies, chemicals, electrical energy, heat, chilly, pathogenic micro-organisms or pathogens, radiation. In a easy inflammatory process corresponding to a surgical incision, the blood supply to the area is increased. When no pathogens are current irritation subsides; the white blood cells devour lifeless cells (phagocytosis) and return to the blood stream. When inflammation is caused by pathogenic organisms, the identical defensive response begins. After leaving the blood steam, the leukocytes (white blood cells) attempt to kill invading organisms. Antitoxins and antibodies are two necessary immune substances which are carried to the realm by the blood. If immune substances and leukocytes are strong sufficient to kill the organisms, inflammation begins to disappear. When these attain the lymph nodes, specialised cells throughout the nodes try to render the micro organism harmless. Local signs of irritation are redness and swelling as a end result of the elevated blood provide plus warmth and pain. General symptoms of irritation are fever, elevated pulse and respiration fee, headache, dry skin, flushed cheeks, elevated white blood cell depend and malaise. Parasites: are organisms which live in or on one other animal, relying on the host for nourishment. Degenerative diseases: are due to deterioration in the operate of organs from atrophy or even necrosis (death of tissues). The term is normally restricted to diseases of old age for which no specific cause has been determined, for example arterial disease similar to hardening of the arteries (arteriosclerosis). Infection: micro organism and viruses are the commonest causative agents in infections. Bacteria are microorganisms, tiny dwelling our bodies visible only through a microscope. Those that are usually not harmful to cells and tissues are called nonpathogenic organisms. Pathogenic bacteria are divided into teams in accordance with their shape: Cocci (round).
Real Experiences: Customer Reviews on Colchicine
Emet, 33 years: They stimulate contraction of the muscular wall and inhibit the motion of the sphincter vesicae. It has two somewhat heavy cusps that permit blood to move freely from the left 261 Human Anatomy and Physiology atrium into the left ventricle. Disproportionate over-investigation might enhance child and household anxiety with out including value to the diagnostic course of.
Shawn, 45 years: Inactivity in a shortened place leads to an increase in connective tissue, an increase in stiffness and resistance to passive stretch (Williams & Goldspink 1973). Study the following word parts pertaining to the constructions of the female reproductive system. This transverse section via the stomach reveals the place of the spleen relative to some other viscera.
Candela, 52 years: The extreme end-diastolic pressures inflicting congestive symptoms and the lowered ranges of cardiac efficiency leading to low-output symptoms are shown by the yellow and blue areas respectively. It serves primarily for muscle attachments and thus is basically surrounded by muscular tissues. The flexor retinaculum is attached laterally to the trapezium and scaphoid bones, and medially to the hamate and pisiform bones.
Kalesch, 37 years: The premotor cortex is extra lateral, whereas the supplemental motor area is more medial and superior. Articular unions that connect the heads of the ribs with the vertebral our bodies and intervertebral discs. These antibodies are overexpressed in autoimmune situations, owing to a wide selection of components, including genetic predisposition and environmental triggers corresponding to infection.
8 of 10 - Review by X. Lukar
Votes: 233 votes
Total customer reviews: 233
References
- Chen HI, Malhotra NR, Oddo M, Heuer GG, Levine JM, LeRoux PD. Barbiturate infusion for intractable intracranial hypertension and its effect on brain oxygenation. Neurosurgery. 2008;63:880-6.
- Kunimoto D, Long R: Tuberculosis: still overlooked as a cause of community- acquired pneumonia-how not to miss it. Respir Care Clin N Am 11:25-34, 2005.
- Olivier A. Extratemporal resections in the surgical treatment of epilepsy. In Spencer SS, Spencer DD (eds), Contemporary Issues in Neurological Surgery. Surgery for Epilepsy. Boston, MA: Blackwell Scientific, pp. 150-167, 1991.
- Fisher CM. Ataxic hemiparesis. Arch Neurol 1978;35:126.
- Gillum RF: Epidemiology of stroke in Hispanic Americans, Stroke 26(9):1707-1712, 1995.
- Scheer B, Perel A, Pfeiffer UJ: Clinical review: Complications and risk factors of peripheral arterial catheters used for haemodynamic monitoring in anaesthesia and intensive care medicine, Crit Care 6:199, 2002.


