Lissa Sugeng, MD, MPH
- Associate Professor of Medicine
- Section of Cardiovascular Medicine
- Yale School of Medicine
- New Haven, CT
Ethambutol dosages: 800 mg, 600 mg, 400 mg
Ethambutol packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Order ethambutol
The human body has 10 physiological organ methods: integumentary, musculoskeletal, respiratory, digestive, urinary, immune, circulatory, nervous, endocrine, and reproductive. The teleological strategy to physiology explains why occasions happen; the mechanistic method explains how they occur. Translational research applies the outcomes of primary physiological research to medical issues. The 4 key themes in physiology are structure/function relationships, similar to molecular interactions and compartmentation; organic power use; information move within the body; and homeostasis. The easiest homeostatic control takes place at the tissue or cell stage and is called local management. Control systems have three parts: an input signal, an integrating middle, and an output signal. The sensor is linked by the input signal to the integrating heart that decides what motion to take. The output sign travels from the integrating center to a target that carries out the suitable response. In adverse suggestions, the response opposes or removes the original stimulus, which in turn stops the response loop. In positive feedback loops, the response reinforces the stimulus quite than reducing or eradicating it. This destabilizes the system until some intervention or occasion outside the loop stops the response. Feedforward control permits the body to predict that a change is about to occur and begin the response loop in anticipation of the change. Regulated variables that change in a predictable method are referred to as biological rhythms. In scientific experimentation, the issue manipulated by the investigator is the impartial variable, and the noticed factor is the dependent variable. All well-designed experiments have controls to be certain that noticed modifications are because of the experimental manipulation and not to some outside factor. Data, the data collected throughout an experiment, are analyzed and introduced, usually as a graph. In addition, ethical questions might come up when utilizing people as experimental topics. To management many experiments, some topics take an inactive substance generally recognized as a placebo. Placebo and nocebo effects, during which modifications happen even when the therapy is inactive, may affect experimental outcomes. In a doubleblind research, a 3rd party removed from the experiment is the one one who knows which group is the experimental group and which is the management. In a crossover examine, the control group in the first half of the experiment turns into the experimental group in the second half, and vice versa. What are the two characteristic options of interacting molecules that decide their organic perform Try to include features of all parts on the map and keep in thoughts that some buildings might share functions. List the four major physiological concerns (themes) which are essential for a dwelling organism to function normally. Put the next components of a reflex within the appropriate order for a physiological response loop: input sign, integrating center, output signal, response, sensor, stimulus, target. The name for day by day fluctuations of physique features such as blood stress, temperature, and metabolic processes is a(n). Which techniques exchange materials with the external surroundings, and what do they exchange Explain the differences amongst constructive feedback, adverse feedback, and feedforward mechanisms.
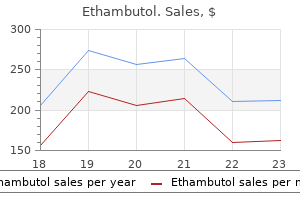
Purchase genuine ethambutol online
This pressure gradient is analogous this expression says that flow is inversely proportional to resistance: if resistance will increase, flow decreases; and if resistance decreases, circulate will increase. For fluid flowing via a tube, resistance is influenced by three elements: the radius of the tube (r), the length of the tube (L), and the viscosity (thickness) of the fluid (, the Greek letter eta). Higher P Flow P1 P1 - P2 = P P2 a hundred mm Hg Flow P = one hundred - seventy five = 25 mm Hg forty mm Hg Flow P = 0, so no circulate. If the pressure gradient remains constant, then flow varies inversely with resistance. Drinking water via a straw is easier than consuming a thick milkshake (resistance increases with viscosity). And consuming the milkshake via a fat straw is way easier than via a thin cocktail straw (resistance will increase as radius decreases). How vital are tube length, fluid viscosity, and tube radius to blood flow in a normal particular person The size of the systemic circulation is decided by the anatomy of the system and is basically constant. Blood viscosity is decided by the ratio of red blood cells to plasma and by how a lot protein is in the plasma. Normally, viscosity is fixed, and small adjustments in both length or viscosity have little impact on resistance. This leaves modifications within the radius of the blood vessels as the primary variable that affects resistance in the systemic circulation. Which is more important for figuring out circulate via a tube: absolute strain or the pressure gradient Because flow is inversely proportional to resistance, move will increase 16-fold when the radius doubles. Similarly, a small change in the radius of a blood vessel has a large impact on the resistance to blood move supplied by that vessel. A lower in blood vessel diameter is named vasoconstriction vas, a vessel or duct. Vasoconstriction decreases blood flow through a vessel, and vasodilation will increase blood circulate through a vessel. Velocity Depends on the Flow Rate and the Cross-Sectional Area the word move is usually used imprecisely in cardiovascular physiology, leading to confusion. Flow normally means flow fee, the quantity of blood that passes a given level in the system per unit time. In the circulation, flow is expressed in both liters per minute (L/min) or milliliters per minute (mL/min). For instance, blood move via the aorta of a 70-kg man at rest is about 5 L/min. In distinction, flow rate measures how much (volume) blood flows previous some extent in a given time frame. The variety of folks passing which, translated into phrases, says that the circulate of blood within the cardiovascular system is directly proportional to the pressure Cardiac Muscle and the Heart 467 the door in 1 minute is the flow rate of individuals via the hallway. In a tube of fixed diameter (and thus fastened cross-sectional area), velocity is immediately related to flow price. In a tube of variable diameter, if the move fee is constant, velocity varies inversely with the diameter. In different phrases, velocity is faster in slim sections, and slower in wider sections. The vessel in the figure has variable width, from narrow, with a cross-sectional area of 1 cm2, to broad, with a cross-sectional space of 12 cm 2. The circulate price is identical alongside the size of the vessel: 12 cm3 per minute (1 cm3 = 1 cubic centimeter (cc) = 1 mL). This flow fee implies that in 1 minute, 12 cm3 of fluid flow past level X in the slender part, and 12 cm3 of fluid flow previous level Y in the broad part. Where the stream is slender, the leaf strikes rapidly, carried by the fast velocity of the water. In sections where the stream widens right into a pool, the rate of the water decreases and the leaf meanders extra slowly.
Diseases
- Chromosome 13 Chromosome 15
- Medium-chain Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
- Pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis
- Ovarian dwarfism
- Albinism immunodeficiency
- Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency
- Myositis
- Hyperglycemia
- Cartwright Nelson Fryns syndrome
- Hypercholesterolemia due to arg3500 mutation of Apo B-100
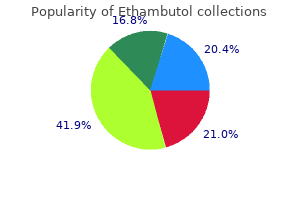
Purchase ethambutol paypal
Most people have experienced encountering a smell that abruptly brings back a flood of recollections of locations or people from the previous. Stimuli bombard your sensory receptors constantly, but your mind can filter out and "flip off " some stimuli. You experience a change in perceptual threshold when you "tune out" the radio whereas studying or when you "zone out" during a lecture. Decreased perception of a stimulus, or habituation, is accomplished by inhibitory modulation [p. If the modulated stimulus all of a sudden becomes important, similar to when the professor asks you a 338 chaPter 10 Sensory Physiology fiG. Gustatory cortex Primary somatic sensory cortex Olfactory cortex Olfactory bulb Auditory cortex Visual cortex Olfactory pathways from the nostril project through the olfactory bulb to the olfactory cortex. At that point, your aware mind seeks to retrieve and recall current sound enter from your subconscious so as to reply the query. The attributes of the stimulus should somehow be preserved as quickly as the stimulus enters the nervous system for processing. Vertigo is a false sensation of spinning motion that patients typically describe as dizziness. Q1: In which part of the mind is sensory information about equilibrium processed For example, some neurons reply most strongly to touch; others respond to adjustments in temperature. For occasion, colour vision is divided into red, blue, and green based on the wavelengths that almost all strongly stimulate the totally different visible receptors. General Properties of Sensory Systems 339 In addition, the brain associates a signal coming from a particular group of receptors with a specific modality. This 1:1 affiliation of a receptor with a sensation is recognized as labeled line coding. Stimulation of a chilly receptor is always perceived as cold, whether the actual stimulus was chilly or a man-made depolarization of the receptor. The blow to the attention that causes us to "see" a flash of light is one other instance of labeled line coding. The sensory areas of the cerebrum are highly organized with respect to incoming indicators, and input from adjoining sensory receptors is processed in adjoining regions of the cortex. This arrangement preserves the topographical group of receptors on the pores and skin, eye, or other regions in the processing centers of the mind. For instance, contact receptors in the hand project to a selected space of the cerebral cortex. Instead, the mind makes use of the timing of receptor activation to compute a location, as shown in fiGure 10. A sound originating instantly in entrance of a person reaches each ears simultaneously. A sound originating on one aspect reaches the nearer ear a quantity of milliseconds earlier than it reaches the other ear. Lateral inhibition, which will increase the distinction between activated receptive fields and their inactive neighbors, is one other means of isolating the placement of a stimulus. A pin pushing on the pores and skin prompts three major sensory neurons, every of which releases neurotransmitters onto its corresponding secondary neuron. The secondary neuron closest to the stimulus (neuron B) suppresses the response of the secondary neurons lateral to it. The inhibition of neurons farther from the stimulus enhances the distinction between the center and the sides of the receptive area, making the sensation extra simply localized. Only essentially the most sensitive receptors (those with the lowest thresholds) respond to a low-intensity stimulus. Once stimulus depth exceeds threshold, the first sensory neuron begins to hearth motion potentials. As stimulus intensity will increase, the receptor potential amplitude (strength) increases in proportion, and the frequency of action potentials within the major sensory neuron will increase, as much as a most price (fiG. The responses of major sensory neurons A, B, and C are proportional to the intensity of the stimulus in every receptor area.
Buy generic ethambutol 800mg
In a neural pathway, such because the pin contact above, the enter signal is electrical and chemical information transmitted by a sensory neuron. Integrating centers actually "earn their pay," nevertheless, when two or more conflicting alerts are available from different sources. The center 210 should consider every sign on the premise of its strength and importance and must provide you with an acceptable response that integrates information from all contributing receptors. In the nervous system, the output sign is at all times the electrical and chemical indicators transmitted by an efferent neuron. Because all electrical signals traveling by way of the nervous system are equivalent, the distinguishing attribute of the signal is the anatomical pathway of the neuron-the route via which the neuron delivers its signal. For instance, the vagus nerve carries neural indicators to the guts, and the phrenic nerve carries neural alerts to the diaphragm. Output pathways in the nervous system are given Homeostatic Reflex Pathways 211 the anatomical name of the nerve that carries the sign. For instance, we speak of the vagal control of coronary heart fee (vagal is the adjective for vagus). In the endocrine system, the anatomical routing of the output sign is all the time the same-all hormones travel within the blood to their goal. Hormonal output pathways are distinguished by the chemical nature of the sign and are therefore named for the hormone that carries the message. For instance, the output signal for a reflex built-in by way of the endocrine pancreas might be both the hormone insulin or the hormone glucagon, relying on the stimulus and the suitable response. Control Systems Vary in Their Speed and Specificity Physiological reflex management pathways are mediated by the nervous system, the endocrine system, or a mixture of the 2 (fig. Reflexes mediated solely by the nervous system or solely by the endocrine system are comparatively simple, however some pathways mix neural and endocrine reflexes and could be quite advanced. The targets of neural pathways may be any sort of muscle, endocrine or exocrine glands, or adipose tissue. Targets of an endocrine pathway are the cells that have the correct receptor for the hormone. In this instance, the blood vessel smooth muscle contracts in response to neurotransmitter binding. In our instance, contraction of smooth muscle tissue within the blood vessel wall decreases the diameter of the blood vessel and decreases circulate by way of this blood vessel. Finally, the extra basic systemic response describes what those particular mobile and tissue events mean to the organism as an entire. In this instance, when the blood vessels constrict, the systemic response is a rise in blood strain. Special cells in the pancreas known as beta cells monitor blood glucose concentrations, and so they launch insulin when blood glucose increases after a meal. Q5: In the insulin reflex pathway, name the stimulus, the sensor, the integrating center, the output sign, the target(s), and the response(s). Target Target Endocrine integrating middle Response Response Output sign # 2: hormone Target Response one hundred ninety 193 206 207 211 213 215 212 ChaPteR 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis taBle 6. Electrical signal that passes by way of neuron, then chemical neurotransmitters that carry the sign from cell to cell. Nature of the signal Speed Duration of action Coding for stimulus depth Distribution of the sign and onset of action are much slower than in neural responses. With a lot overlap between pathways controlled by the nervous and endocrine methods, it is smart to consider these methods as components of a continuum rather than as two discrete techniques. Anatomically, we are in a position to isolate a neuron and hint it from its origin to where it terminates on its goal. Endocrine management is more general as a outcome of the chemical messenger is released into the blood and may attain virtually every cell in the body. Specificity Neural control is very specific as a end result of every neuron Speed Neural reflexes are much sooner than endocrine re- nature of the Signal the nervous system makes use of both electrical and chemical signals to send data throughout the physique. Electrical signals travel lengthy distances via neurons, releasing chemical signals (neurotransmitters) that diffuse across the small gap between the neuron and its target. In a limited variety of instances, electrical signals cross instantly from cell to cell via gap junctions. The endocrine system makes use of only chemical signals: hormones secreted into the blood by endocrine glands or cells. In a neuroendocrine pathway, a neuron creates an electrical sign, however the chemical released by the neuron is a neurohormone that goes into the blood for common distribution.
Buy generic ethambutol canada
Which is more prone to cross a cell membrane by simple diffusion: a fatty acid molecule or a glucose molecule Compartment A is full of an aqueous answer of yellow dye, and compartment B is filled with an aqueous answer of an equal concentration of blue dye. Instead, the overwhelming majority of solutes cross membranes with the assistance of membrane proteins, a course of we call mediated transport. Membrane Proteins Have Four Major Functions Protein-mediated transport across a membrane is carried out by membrane-spanning transport proteins. For physiologists, classifying membrane proteins by their perform is more useful than classifying them by their construction. Our useful classification scheme acknowledges 4 broad categories of membrane proteins: (1) structural proteins, (2) enzymes, (3) receptors, and (4) transport proteins. Structure Function Integral proteins Peripheral proteins Membrane transport Structural proteins are part of Membrane enzymes activate Membrane receptors are active in Carrier proteins change conformation Channel proteins Cell junctions Cytoskeleton are energetic in form Receptormediated endocytosis Open channels Gated channels Metabolism Signal transfer open and close Mechanically gated channel Voltage-gated channel Chemically gated channel 1. They connect cells to the extracellular matrix by linking cytoskeleton fibers to extracellular collagen and different protein fibers [p. For instance, enzymes on the external floor of cells lining the small gut are liable for digesting peptides and carbohydrates. Enzymes connected to the intracellular floor of many cell membranes play an necessary function in transferring signals from the extracellular environment to the cytoplasm [see Chapter 6]. The binding of a receptor with its ligand normally triggers one other event on the membrane (fig. Sometimes the ligand remains on the cell surface, and the receptor-ligand complicated triggers an intracellular response. In different situations, the receptor-ligand complicated is brought into the cell in a vesicle [p. A second way to classify transport* acknowledges two major types of transport proteins: channels and carriers (fig. Channel proteins create water-filled passageways that directly hyperlink the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Carrier proteins, also simply known as transporters, bind to the substrates that they carry but by no means form a direct connection between the intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid. Channel proteins allow extra rapid transport throughout the membrane however typically are limited to shifting small ions and water. Extracellular fluid Receptor-ligand advanced brought into the cell e Cell membran Receptor Events in the cell Intracellular fluid Cytoplasmic vesicle Carriers, while slower, can transfer bigger molecules than channels can. Channel Proteins Form Open, Water-Filled Passageways Channel proteins are made of membrane-spanning protein subunits that create a cluster of cylinders with a tunnel or pore via the middle. In this guide, we limit use of the time period channel to smaller channels whose facilities are narrow, water-filled pores (fig. When water-filled ion channels are open, tens of hundreds of thousands of ions per second can whisk via them unimpeded. Ion channels may be specific for one ion or could enable ions of comparable size and cost to pass. For instance, there are Na+ channels, K+ channels, and nonspecific monovalent ("one-charge") cation channels that transport Na+, K+ and lithium ions Li+. The selectivity of a channel is decided by the diameter of its central pore and by the electrical charge of the amino acids that line the channel. If the channel amino acids are positively charged, optimistic ions are repelled and negative ions can move via the channel. On the opposite hand, a cation channel should have a adverse cost that draws cations but prevents the passage of Cl- or different anions. The open or closed state of a channel is set by areas of the protein molecule that act like swinging "gates. Channels can be categorised in accordance with whether their gates are often open or often closed. Open channels spend most of their time with their gate open, allowing ions to transfer forwards and backwards across the membrane with out regulation. Open channels are typically known as both leak channels or pores, as in water pores.
Purchase ethambutol with visa
When the chest volume decreases, alveolar stress will increase, and air flows out into the atmosphere. This motion of air is bulk move as a result of the complete fuel mixture is transferring somewhat than merely one or two of the gases in the air. Gases, singly or in a combination, move from areas of upper pressure to areas of decrease stress. Vital capacity represents the utmost amount of air that could be voluntarily moved into or out of the respiratory system with one breath. Vital capability decreases with age as muscular tissues weaken and the lungs become less elastic. Other capacities of significance in pulmonary medication embrace the inspiratory capability (tidal quantity + inspiratory reserve volume) and the useful residual capability (expiratory reserve volume + residual volume). Inspiration Occurs When Alveolar Pressure Decreases For air to transfer into the alveoli, stress inside the lungs should turn into decrease than atmospheric pressure. During inspiration, thoracic quantity increases when certain skeletal muscular tissues of the rib cage and diaphragm contract. Contraction of the diaphragm causes between 60% and 75% of the inspiratory quantity change during normal quiet respiration. Rib movement throughout inspiration has been likened to a pump handle lifting up and away from the pump (the ribs transferring up and away from the spine) and to the motion of a bucket handle because it lifts away from the aspect of a bucket (ribs shifting outward in a lateral direction). For many years, quiet respiratory was attributed solely to the action of the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscular tissues. It was thought that the scalenes and sternocleidomastoid muscular tissues have been active only throughout deep respiration. In latest years, nonetheless, studies have changed our understanding of how these accent muscles contribute to quiet respiration. Observation of sufferers with neuromuscular issues has revealed that although the contracting diaphragm increases thoracic volume by transferring towards the belly cavity, it also tends to pull the lower ribs inward, working in opposition to inspiration. In regular people, we know that the decrease ribs transfer up and out during inspiration somewhat than inward. New evidence additionally downplays the role of the external intercostal muscular tissues throughout quiet respiratory. However, the exterior intercostals play an increasingly necessary position as respiratory exercise will increase. Because the precise contribution of exterior intercostals and scalenes varies relying on the type of respiration, we group these muscles together and easily name them the inspiratory muscular tissues. Negative numbers designate subatmospheric pressures, and constructive numbers denote higherthan-atmospheric pressures. In the brief pause between breaths, alveolar strain is the identical as atmospheric strain (0 mm Hg at point A1). During Ventilation, Air Flows due to Pressure Gradients Breathing is an energetic course of that requires muscle contraction. Air flows into the lungs due to strain gradients created by a pump, just as blood flows due to the pumping action of the guts. In the respiratory system, muscle tissue of the thoracic cage and diaphragm perform as the pump because most lung tissue is skinny change epithelium. When these muscles contract, the lungs broaden, held to the within of the chest wall by the pleural fluid. The primary muscles involved in quiet respiration (breathing at rest) are the diaphragm, the exterior intercostals, and the scalenes. During pressured respiration, other muscles of the chest and stomach could also be recruited to assist. Examples of physiological conditions in which breathing is pressured embody train, playing a wind instrument, and blowing up a balloon. As we noted earlier within the chapter, air move in the respiratory tract obeys the same rule as blood circulate: Flow P>R this equation implies that (1) air flows in response to a stress gradient (�P) and (2) move decreases as the resistance (R) of the system to move will increase. Compare the course of air movement throughout one respiratory cycle with the path of blood circulate throughout one cardiac cycle. Explain the relationship between the lungs, the pleural membranes, the pleural fluid, and the thoracic cage. Side view: "Pump deal with" movement will increase anterior-posterior dimension of rib cage.
Baccharis genistelloides (Carqueja). Ethambutol.
- Are there any interactions with medications?
- Protecting the liver, diabetes, heart pain (angina), improving circulation, and other conditions.
- Are there safety concerns?
- What is Carqueja?
- Dosing considerations for Carqueja.
- How does Carqueja work?
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=97071
Cheap ethambutol 400 mg online
Evans is given tetanus antitoxin to deactivate any toxin that has not but entered motor neurons. She additionally receives penicillin, an antibiotic that kills the micro organism, and medicines to help loosen up her muscular tissues. Ling calls in the chief of anesthesiology to administer metocurine, a drug similar to curare. Patients receiving metocurine have to be placed on respirators that breathe for them. For folks with tetanus, nevertheless, metocurine can briefly halt the muscle spasms and allow the physique to recuperate. Most physique movements are highly built-in, coordinated responses that require input from multiple areas of the brain. Movement Can Be Classified as Reflex, Voluntary, or Rhythmic Movement could be loosely classified into three classes: reflex movement, voluntary movement, and rhythmic motion (tBl. However, like other spinal reflexes, reflex actions can be modulated by enter from larger mind centers. In addition, the sensory input that initiates reflex actions, such as the enter from muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs, goes to the brain and participates in the coordination of voluntary actions and postural reflexes. Postural reflexes help us maintain body position as we stand or move through house. They require steady sensory input from visual and vestibular (inner ear) sensory systems and from the muscles themselves. Muscle, tendon, and joint receptors provide information about proprioception, the positions of assorted body components relative to each other. You can inform if your arm is bent even when your eyes are closed as a end result of these receptors present details about body place to the mind. Information from the vestibular equipment of the ear and visible cues help us preserve our position in area. For example, we use the horizon to tell us our spatial orientation relative to the ground. People making an attempt to move in a darkish room instinctively reach for a wall or piece of furniture to assist orient themselves. The lack of cues is what makes flying airplanes in clouds or fog impossible with out devices. The impact of gravity on the vestibular system is such a weak enter compared with visual or tactile cues that pilots might discover themselves flying the incorrect method up relative to the bottom. They require integration on the cerebral cortex, and they can be initiated at will with out external stimuli. Learned voluntary movements improve with practice, and some even become involuntary, like reflexes. It might have been tough at first however when you discovered to pedal easily and to keep your stability, the movements turned automatic. Changes in rhythmic exercise, such as altering from strolling to skipping, are additionally initiated by input from the cerebral cortex. It continues its repetitive hopping till somebody turns it off (or till the battery runs down). In humans, rhythmic movements controlled by central sample mills include locomotion and the unconscious rhythm of quiet breathing. The capability of central pattern generators to sustain rhythmic motion without continued sensory input has proved necessary for research on spinal twine accidents. The precision of voluntary actions improves with follow, but so does that of some reflexes. In addition, most voluntary movements require steady input from postural reflexes. Feedforward reflexes enable the body to prepare for a voluntary motion, and feedback mechanisms are used to create a clean, steady movement. The thalamus relays and modifies indicators as they cross from the spinal twine, basal ganglia, and cerebellum to the cerebral cortex (tBl.
Buy discount ethambutol 600 mg on line
In addition, cardiac muscle is underneath sympathetic and parasympathetic control in addition to hormonal control. You will learn more about cardiac muscle and how it functions throughout the coronary heart whenever you study the cardiovascular system. Now verify your understanding of this running problem by evaluating your solutions with the information within the following abstract table. The periodic paralyses are a household of associated issues caused by muscle ion channel mutations. Read the information there to examine the Question Q1: When Na+ channels on the muscle membrane open, which method does Na+ transfer Q3: What ion is answerable for the repolarization part of the muscle action potential, and during which direction does this ion transfer throughout the muscle fiber membrane The resting membrane potential of cells is unfavorable relative to the extracellular fluid. Integration and Analysis the electrochemical gradient causes Na+ to transfer into cells. During repeated contractions, K+ leaves the muscle fiber, which might contribute to elevated extracellular [K+] (hyperkalemia). During an attack, the Na+ channels stay open and constantly admit Na+, and the muscle fiber remains depolarized. The first action potential causes a twitch, but the muscle then goes right into a state of flaccid (uncontracted) paralysis. Mechanical properties of muscle tissue that affect contraction embody elastic elements, such as the protein titin and the sequence elastic parts of the intact muscle. Compartmentation is essential to muscle operate, as demonstrated by the focus of Ca 2+ in the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the necessary thing position of Ca2+ alerts in initiating contraction. The law of mass action is at work within the dynamics of Ca2+-calmodulin and Ca2+-troponin binding and unbinding. Communication happens on a scale as small as electrical signals spreading amongst smooth muscle cells through gap junctions, or as giant as a somatic motor neuron innervating a quantity of muscle fibers. Skeletal muscles are managed only by somatic motor neurons, but easy and cardiac muscle have complex regulation that ranges from neurotransmitters to hormones and paracrine molecules. Cardiac and easy muscle are controlled by autonomic innervation, paracrine indicators, and hormones. Myosin binds to actin, creating crossbridges between the thick and skinny filaments. The sarcomere is divided into I bands (thin filaments only), an A band that runs the size of a thick filament, and a central H zone occupied by thick filaments only. The M line and Z disks represent attachment sites for myosin and actin, respectively. The sliding filament principle of contraction states that in contraction, overlapping thick and thin filaments slide past one another in an energy-dependent manner because of actin-myosin crossbridge motion. This unblocks the myosin-binding sites and allows myosin to complete its power stroke. The latent interval between the top of the muscle motion potential and the beginning of muscle pressure development represents the time required for Ca2+ release and binding to troponin. Aerobic metabolism is very efficient but requires an adequate provide of oxygen to the muscular tissues. Muscle fatigue is a reversible condition by which a muscle is no longer in a position to generate or sustain the anticipated power output. The origin is the top of the muscle connected closest to the trunk or to the more stationary bone. T-tubules permit action potentials to move quickly into the interior of the fiber and release calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Skeletal muscle fibers may be categorised on the basis of their velocity of contraction and resistance to fatigue into slow-twitch (oxidative) fibers, fast-twitch oxidative-glycolytic fibers, and fast-twitch glycolytic fibers. Myoglobin is an oxygen-binding pigment that transfers oxygen to the interior of the muscle fiber. The tension of a skeletal muscle contraction is set by the size of the sarcomeres earlier than contraction begins.
Generic ethambutol 600 mg without a prescription
Because oxidative fibers have Fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscle tissue Slow-twitch oxidative muscle has massive amounts of pink myoglobin, numerous mitochondria, and intensive capillary blood supply, in distinction to fast-twitch glycolytic muscle. The combination of larger dimension, less myoglobin, and fewer blood vessels implies that glycolytic fibers usually tend to run out of oxygen after repeated contractions. Type 2A fast-twitch oxidative-glycolytic fibers exhibit properties of each oxidative and glycolytic fibers. Type 2A fibers, like kind 1 slow-twitch fibers, are classified as purple muscle due to their myoglobin content. Human muscular tissues are a mix of fiber varieties, with the ratio of varieties various from muscle to muscle and from one individual to another. For instance, who would have extra fast-twitch fibers in leg muscle tissue, a marathon runner or a high-jumper Resting Fiber Length Affects Tension In a muscle fiber, the stress developed throughout a twitch is a direct reflection of the length of individual sarcomeres before contraction begins (fig. Each sarcomere contracts with optimum pressure if it is at optimum size (neither too long nor too short) before the contraction begins. Fortunately, the conventional resting length of skeletal muscular tissues normally ensures that sarcomeres are at optimum length when they start a contraction. The sliding filament theory predicts that the tension generated by a muscle fiber is directly proportional to the variety of crossbridges fashioned between the thick and thin filaments. Consequently, the thick filaments can move the skinny filaments only a short distance before the skinny actin filaments from opposite ends of the sarcomere begin to overlap. Thus, the event of single-twitch tension in a muscle fiber is a passive property that is dependent upon filament overlap and sarcomere size. The drive generated by the contraction of a single muscle fiber can be elevated by growing the rate (frequency) at which muscle action potentials stimulate the muscle fiber. If repeated action potentials are separated by lengthy intervals of time, the muscle fiber has time to relax fully between stimuli (fig. This process is named summation and is much like the temporal summation of graded potentials that takes place in neurons [p. If motion potentials continue to stimulate the muscle fiber repeatedly at quick intervals (high frequency), relaxation between contractions diminishes until the muscle fiber achieves a state of maximal contraction often identified as tetanus. Muscle action potentials are initiated by the somatic motor neuron that controls the muscle fiber. Summation in muscle fibers implies that the of the fiber increases with repeated motion potentials. Temporal summation in neurons signifies that the of the neuron increases when two depolarizing stimuli occur shut collectively in time. A Motor Unit Is One Motor Neuron and Its Muscle Fibers the basic unit of contraction in an intact skeletal muscle is a motor unit, composed of a group of muscle fibers that perform collectively and the somatic motor neuron that controls them (fig. When the somatic motor neuron fires an action potential, all muscle fibers in the motor unit contract. Note that though one somatic motor neuron innervates a number of fibers, every muscle fiber is innervated by solely a single neuron. In muscles used for fantastic motor actions, such because the extraocular muscle tissue that transfer the eyes or the muscles of the hand, one motor unit contains as few as three to five muscle fibers. If one such motor unit is activated, just a few fibers contract, and the muscle response is type of small. Tension Tension One twitch Summed twitches 12 zero 100 200 300 400 500 zero a hundred 200 300 four hundred 500 Ca2+ signal Contractionrelaxation Muscle twitch Time (msec) Time (msec) (c) Summation Leading to Unfused Tetanus: Stimuli are far sufficient apart to permit muscle to loosen up barely between stimuli. Unfused tetanus Maximum tension (d) Summation Leading to Complete Tetanus: Muscle reaches steady pressure. Complete tetanus Maximum rigidity Tension Single-twitch pressure zero Time (msec) Time (msec) Fatigue causes muscle to lose tension regardless of continuing stimuli. The gastrocnemius muscle within the calf of the leg, for example, has about 2000 muscle fibers in every motor unit. Each time a further motor unit is activated in these muscular tissues, many extra muscle fibers contract, and the muscle response jumps by correspondingly higher increments. Which sort of muscle fiber associates with a specific neuron seems to be a perform of the neuron.
Buy generic ethambutol line
If we assume that normal total body osmolarity is 300 mOsM and that the volume of fluid in the physique is forty two L, the addition of 155 milliosmoles of Na+ and one hundred fifty five milliosmoles of Cl- would improve whole body osmolarity to 307 mOsM*-a substantial improve. Fortunately, our homeostatic mechanisms normally preserve mass steadiness: Anything extra that comes into the body is excreted. Vasopressin launch causes the kidneys to preserve water (by reabsorbing water from the filtrate) and concentrate the urine. For many years scientists thought urea crossed cell membranes solely by passive transport. However, lately, researchers have discovered that membrane transporters for urea are present within the collecting duct and loops of Henle. One household of transporters consists of facilitated diffusion carriers, and the opposite family has Na+dependent secondary lively transporters. These urea transporters apparently help focus urea within the medullary interstitium, the place it contributes to the high interstitial osmolarity. Q4: One approach to estimate physique osmolarity is to double the plasma Na+ concentration. This is about 2 teaspoons of salt, or a hundred and fifty five milliosmoles of Na+ and one hundred fifty five milliosmoles of Cl-. Our normal plasma Na+ focus, measured from a venous blood pattern, is 135�145 milliosmoles Na+ per liter of plasma. The kidneys are liable for most Na+ excretion, and usually only a small quantity of Na+ leaves the physique in feces and perspiration. However, in conditions similar to vomiting, diarrhea, and heavy sweating, we could lose important amounts of Na+ and Cl- by way of nonrenal routes. Although we speak of ingesting and losing salt (NaCl), only renal Na+ absorption is regulated. And truly, the stimuli that set the Na+ stability pathway in movement are more closely tied to blood volume and blood pressure than to Na+ ranges. Aldosterone is a steroid hormone synthesized in the adrenal cortex, the outer portion of the adrenal gland that sits atop every kidney [p. Like other steroid hormones, aldosterone is secreted into the blood and transported on a protein service to its goal. The primary web site of aldosterone motion is the last third of the distal tubule and the portion of the accumulating duct that runs by way of the kidney cortex (the cortical amassing duct). In the early response phase, apical Na+ and K+ channels enhance their open time underneath the affect of an as-yet-unidentified signal molecule. Note that Na+ and water reabsorption are separately regulated within the distal nephron. In distinction, Na+ reabsorption within the proximal tubule is routinely followed by water reabsorption because the proximal tubule epithelium is at all times freely permeable to water. If a person experiences hyperkalemia, what occurs to resting membrane potential and the excitability of neurons and the myocardium Aldosterone Controls Sodium Balance the regulation of blood Na+ levels takes place via some of the sophisticated endocrine pathways of the body. The reabsorption of Na+ in the distal tubules and collecting ducts of Low Blood Pressure Stimulates Aldosterone Secretion What controls physiological aldosterone secretion from the adrenal cortex Blood Interstitial fluid P cell of distal nephron Lumen of distal nephron 1 Aldosterone combines with a cytoplasmic receptor. Finally, at the distal nephron, aldosterone initiates the intracellular reactions that cause the tubule to reabsorb Na+. Sympathetic neurons, activated by the cardiovascular management center when blood strain decreases, terminate on the granular cells and stimulate renin secretion. Paracrine feedback-from the macula densa within the distal tubule to the granular cells-stimulates renin release [p. When fluid flow through the distal tubule is comparatively high, the macula densa cells release paracrine signals that inhibit renin launch. When fluid circulate within the distal tubule decreases, macula densa cells signal the granular cells to secrete renin.
References
- Wang M, Gu XY, Yen WB, et al: Randomized clinical trial on the combination of preoperative irradiation and surgery in the treatment of esophageal carcinoma: Report on 206 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 16:325, 1989.
- Carr LK, Webster GD: Abdominal repair of vesicovaginal fistula, Urology 48(1):10n11, 1996.
- Kuure S, Chi X, Lu B, et al: The transcription factors Etv4 and Etv5 mediate formation of the ureteric bud tip domain during kidney development, Development 137:1975, 2010.
- Gudmundsson J, Sulem P, Gudbjartsson DF, et al: A study based on wholegenome sequencing yields a rare variant at 8q24 associated with prostate cancer, Nat Genet 44(12):1326n1329, 2012.
- Fraga GP, Bansal V, Coimbra R. Transfusion of blood products in trauma: an update. J Emerg Med. 2010;39:253-260.
- Chambers BR, Donnan GA. Carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005;CD001923.