JoAnne M. Foody, MD, FACC, FAHA
- Editor-in-Chief, CardioSmarts.org
- Director of the Cardiovascular Wellness Center
- Staff Physician, Chief of the Division of
- Preventive Medicine, Brigham and Women? Hospital
- Associate Professor of Internal Medicine
- Harvard Medical School
- Boston, Massachusetts
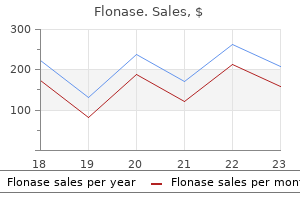
Flonase dosages: 50 mcg
Flonase packs: 1 nasal sprays, 2 nasal sprays, 3 nasal sprays, 4 nasal sprays, 5 nasal sprays, 6 nasal sprays, 7 nasal sprays, 8 nasal sprays, 9 nasal sprays, 10 nasal sprays

Cheap flonase 50 mcg without prescription
The gland could also be destroyed by hemorrhage with meningococcal infection, or by viral, tubercular, or histoplasmosis infections. The main results of these hormonal deficits embrace decreased blood glucose ranges, poor stress response, fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections. Low serum sodium focus, decreased blood volume, and hypotension, accompanied by excessive potassium levels, result from the mineralocorticoid (aldosterone) deficit and lead to cardiac arrhythmias and failure. Analysis of arterial blood gases signifies that his serum bicarbonate level is low, and his serum pH is just under regular range. At that point, he was chubby, enjoyed foods with high carbohydrate and fat content, and led a sedentary life. Weight loss, acceptable food regimen, and train have been really helpful to cut back blood glucose levels. He has simply been admitted to the hospital with severe pyelonephritis, a kidney an infection. Why is persistent elevated blood stress a severe concern in a affected person (see Chapter 18) How does hypercalcemia cause renal calculi, and how do renal calculi cause extreme ache (see Chapter 21) Dietary restrictions on calcium consumption and increased fluid intake have been beneficial to scale back the risk of additional calculi. Following a routine checkup and laboratory tests 2 years later, simvastatin (Zocor) was prescribed. A combination of metformin and rosiglitazone has been prescribed in addition to regular train and cautious dietary management. Peripheral neuropathy with complete loss of sensory function had developed in each feet. Orthopedic sneakers had been ordered and arrangements made for a podiatrist to provide regular foot care. At this time physique weight had once more elevated substantially and blood strain was elevated. Fosinopril (Monopril) was prescribed, together with recommendations for weight loss and regular exercise. At age 60, routine monitoring throughout a workout on the well being club indicated atrial fibrillation. During session, the heart specialist additionally noted his blood strain was very high. State the aim of the following drugs prescribed presently (see Chapter 18): fosinopril (Monopril), atorvastatin (Lipitor), amlodipine (Norvasc), warfarin (Coumadin), and sotalol (Sotacor). Since that time, continued common train and dietary modification have maintained weight at recommended levels. Blood strain is within normal vary, HbA1c is under 7 and atrial fibrillation is controlled. She had been handled for carpal tunnel syndrome three years earlier than, and she or he had famous an increase in hand and foot sizes over the previous several years. In the previous week, she had skilled severe complications associated with nausea and vomiting. Blood checks indicated low ranges of thyroxine, cortisol, and gonadotropins, but high levels of growth hormone. The acute episode had resulted from infarction of the pituitary gland (pituitary apoplexy). Following supply of the second youngster, blood stress and blood glucose remained elevated in C. In addition to common train, metformin was prescribed and a nutritionist developed an applicable food regimen. Briefly describe how diet, exercise, and this drug each contribute to reduction of blood glucose. Thyroxine and cortisol levels have been low regular; no alternative therapy was beneficial right now. Explain the rationale for the neurologic indicators and signs resulting in admission (see Chapter 22). Also complications had turn out to be more frequent and have been accompanied by visible indicators similar to spatial distortion.
Purchase flonase with amex
Suspected periodontopathogens in erupting third molar websites of periodontally wholesome people. The etiology of late decrease arch crowding different to mesially directed forces: a evaluation. Lower third molar improvement in relation to skeletal maturity and chronological age. Tooth measurement, spacing, and crowding in relation to eruption or impaction of third molars. Radiographic assessment of maxillary canine eruption in kids with medical indicators of eruption disturbance. Image accuracy of plain movie radiography and computerized tomography in assessing morphological abnormality of impacted enamel. A long-term, follow-up, radiographic analysis of asymptomatic impacted third molars in orthodontically treated sufferers. Pathologically significant pericoronal lesions in adults: histopathologic analysis. Incidence of enormous third-molar�associated cystic lesions requiring hospitalization. A examine of sports-related mandibular angle fracture: relation to the place of the third molars. Relationship between fractures of the mandibular angle and the presence and state of eruption of the lower third molar. Safety of coronectomy versus excision of knowledge enamel: a randomized controlled trial. The eruption tendency and modifications of path of impacted teeth following surgical publicity. The impact of two alternative methods of canine exposure upon subsequent period of orthodontic remedy. Closed eruption surgical technique for impacted maxillary incisors: a postorthodontic periodontal evaluation. Surgical exposure and bracketing approach for uprighting impacted mandibular second molars. Impacted third molars: radiographic features used to predict extraction difficulty. Textbook and Color Atlas of Tooth Impactions: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. Assessment of the lingual nerve in the third molar area utilizing magnetic resonance imaging. Prophylactic use of phenoxymethylpenicillin and tinidazole in mandibular third molar surgical procedure, a comparative placebo controlled medical trial. Effect of antibiotic treatment on postoperative infections after surgical removal of mandibular third molars. Effect of tinidazole on postoperative issues after surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars. Prevention of postoperative symptoms by basic antibiotic remedy and native bandage in removal of mandibular third molars. Metronidazole (Flagyl) and Arnica Montana within the prevention of post-surgical complications: a comparative placebo managed scientific trial. Relationship between bacterial contamination and alveolitis after third molar surgery. An investigation in to post-operative ache after third molar surgical procedure under native analgesia. The impact of smoking on immediate post-extraction socket filling with blood and the incidence of painful socket. A double-blind research on the effectiveness of tetracycline in decreasing the incidence of fibrinolytic alveolitis. Dysesthesia after mandibular third molar surgical procedure: a retrospective examine and analysis of 1,377 surgical procedures. Prospective examine of dysesthesia following odontectomy of impacted mandibular third molars. Observations on the restoration of sensation following inferior alveolar nerve injuries.
Diseases
- Niemann Pick disease
- Partial deletion of Y
- Cerebellar hypoplasia
- Homocystinuria due to defect in methylation (cbl g)
- Syndrome of inappropraite antidiuretic hormone
- Mesomelic syndrome Pfeiffer type
- Wallerian degeneration
- Short limb dwarfism Al Gazali type
- Taste disorder
- Halal syndrome
Generic flonase 50 mcg visa
The right bronchus is bigger and straighter and due to this fact is the extra likely destination for any aspirated materials. Each main or major bronchus then branches in to many smaller (secondary) bronchi after which in to bronchioles, forming an inverted bronchial "tree. This smooth muscle contracts or relaxes to modify the diameter of the bronchioles. Bronchodilation outcomes when sympathetic stimulation relaxes the smooth muscle, dilating or enlarging the bronchioles. Many elastic fibers are present in the lung tissue, enabling the expansion and recoil of the lungs during air flow. The respiratory mucosa is steady throughout all branches of the bronchi and bronchioles. Air in the bronchioles then flows in to the alveolar ducts and alveoli, or air sacs, which resemble a cluster of grapes. The alveoli are shaped by a single layer of easy squamous epithelial tissue, which promotes the diffusion of gases in to the blood, the end-point for impressed air. The respiratory membrane is the mixed alveolar and capillary wall, a very thin membrane, through which gas trade takes place. There are hundreds of thousands of alveoli, and the capillaries of the pulmonary circulation are in shut contact, providing a really massive floor space for the diffusion of gases. The alveoli include macrophages, whose function is to take away any overseas materials that penetrates to this stage. The inside surfaces of the alveoli are coated with a really small amount of fluid containing surfactant, produced by specialized cells in the alveolar wall. Surfactant has a detergent action that reduces floor pressure of the alveolar fluid (the tendency for fluid to reduce its surface space by forming droplets), facilitating inspiration and preventing complete collapse of the alveoli during expiration. When inspiration is full, the method of expiration reverses airflow within the passageways, forcing air out of the alveoli and up the bronchi, trachea, and nose. The mediastinum is the region within the center of the chest, which incorporates the center, the main blood vessels, the esophagus, and the trachea. The proper lung is split in to three lobes and the left lung in to two lobes because of the place of the guts, and each lobe is then divided in to segments. The lung tissue (lungs, bronchi, and pleurae) is nourished by the bronchial arteries, which department from the thoracic aorta. If atmospheric stress is larger than air strain contained in the lungs, air will transfer from the atmosphere in to the lungs (inspiration). For expiration to happen, strain have to be larger within the lungs than within the environment. These pressure changes in the lungs result from alterations in the measurement of the thoracic cavity. A sequence of events is responsible for the change in dimension of the thorax and the changes in airflow with inspiration and expiration: 1. Normal quiet inspiration begins with contraction of the diaphragm (the primary muscle of inspiration) and the external intercostal muscle tissue. The diaphragm flattens and descends, rising the size of the thoracic cavity. The exterior intercostal muscles raise the ribs and sternum up and outward, rising the transverse and anteroposterior diameters of the thorax. Atmospheric Pressure - 760 mm Hg 327 Intrapleural space Chest wall Intrapleural pressure 756 mmHg Diaphragm Intrapulmonic space�760 mm Hg (pressure of atmosphere) A. Intrapulmonic pressure becomes adverse (usually lower than atmosphere�758 mm Hg) 5. The increased size of the thoracic cavity ends in decreased strain in the pleural cavity and in the alveoli and airways. As the ribs and diaphragm move, the hooked up parietal pleura pulls the adhering visceral pleura and lungs along with it. As the visceral pleura strikes outward, the elastic lungs expand with it, leading to a decrease in air stress contained in the lungs. At this point, atmospheric pressure is bigger than intra-alveolar pressure, so air flows from the environment down the airways in to the alveoli.
Cheap flonase 50mcg fast delivery
A, When eradicating a vertical impaction, the bone on the occlusal, buccal, and distal elements of the crown is removed, and the tooth is sectioned in to mesial and distal parts. If the tooth has a fused single root, the distal portion of the crown is sectioned off in a way just like that depicted for a mesioangular impaction. B, the posterior aspect of the crown is elevated first with a Cryer elevator inserted in to a small buy level within the distal portion of the tooth. A, For a distoangular impaction, the occlusal, buccal, and distal bone is removed with a bur. It is necessary to remember that extra distal bone have to be taken off than for a vertical or mesioangular impaction. B, the crown of the tooth is sectioned off with a bur and is delivered with straight elevator. C, the purchase point is put in to the remaining root portion of the tooth, and the roots are delivered by a Cryer elevator with a wheel-and-axle movement. If the roots diverge, it might be needed in some instances to split them in to impartial portions. The best methodology to accomplish this is to mechanically d�bride the socket and the realm under the flap with a periapical curette. A mosqui to hemostat is normally used carefully to take away any remnant of the dental follicle. Finally, the socket and wound should be completely irrigated with saline or sterile water (30�50 mL is optimal). The flap is returned to its unique place, and the preliminary resorbable suture is positioned at the posterior facet of the second molar. A, Once the delicate tissue has been reflected, a small amount of buccal bone is eliminated with a bur or a hand chisel. B, the tooth is then delivered by a small straight elevator with rotational and lever types of movement. To obtain this objective, prophylactic antibiotics are essential in some surgical procedures. Most of these procedures fall in to the clean-contaminated or contaminated classes of surgical procedure. The incidence of postoperative infections in a clear surgery is expounded extra to operator approach than to using prophylactic antibiotics. Surgery for the elimination of impacted third molars clearly suits in to the category of clean-contaminated surgery; nevertheless, the exact incidence of postoperative infection is unknown. In the identical old sense of the word, an infection most likely is a rare incidence after third molar surgery. In basic, a reliable, experienced surgeon would count on to have an infection rate within the vary of 1% to 5% for all third molar procedures. This disturbance in wound therapeutic is most likely brought on by the mixture of saliva and anaerobic bacteria. The use of prophylactic antibiotics in third molar surgery does, in fact, scale back the incidence of dry socket. Other methods that cut back bacterial contamination of the socket, corresponding to copious irrigation, preoperative rinses with chlorhexidine, and placement of antibiotics in the extraction socket, are also effective. The administration of perioperative steroids might improve the incidence of alveolar osteitis after third molar surgery, but the knowledge are lacking as to the exact degree of enhance. The removal of complete bony impactions is likewise related to elevated postoperative pain and morbidity and a rise in the incidence of inferior alveolar nerve anesthesia. Another determinant of the incidence of issues of third molar surgery is the relative expertise and coaching of the surgeon. The much less experienced surgeon could have a considerably greater incidence of issues than the trained experienced surgeon. All of these are interpreted by the patient as being unpleasant and will, due to this fact, be minimized as a lot as possible. However, despite its extreme importance, this subject has received little vital study. Several authorities have published information on the short-term impression of third molar removing on high quality of life. Large population studies of post�third molar removal healthrelated high quality of life have offered detailed data on the implications of impaction surgery and have make clear predictors of delayed recovery.
Purchase flonase with a visa
Infecting organisms are often Escherichia coli or enterococci, which gain entry to the gallbladder through the sphincter of Oddi or from the portal veins or adjoining lymph nodes. When a stone obstructs bile move in the cystic or widespread bile duct, biliary colic develops, consisting of extreme spasms of ache ensuing from robust muscle contractions trying to move the stone along. Obstruction of the biliary system at the sphincter of Oddi may also cause pancreatitis as a outcome of the pancreatic secretions are backed up or bile refluxes in to the pancreatic ducts. Factors that indicate a high threat for gallstones embrace obesity, excessive ldl cholesterol consumption, multiparity (several children), and using oral contraceptives or estrogen dietary supplements. Bile pigment stones are more common in people with hemolytic anemia, alcoholic cirrhosis, or biliary tract infection. However, bigger calculi may impede a duct at any time, causing sudden severe waves of ache (biliary colic) within the higher proper quadrant of the abdomen or epigastric space, typically radiating to the again and right shoulder. Describe the pain typical of an acute episode of gallstone obstruction and provides the rationale for it. Prehepatic jaundice outcomes from excessive destruction of red blood cells and is characteristic of hemolytic anemias or transfusion reactions. Increased hemolysis of pink blood cells combined with the immature infant liver results in a transient delicate hyperbilirubinemia. Intrahepatic jaundice occurs in people with liver illness, similar to hepatitis or cirrhosis. Posthepatic jaundice is attributable to obstruction of bile circulate in to the gallbladder or duodenum and subsequent backup of bile in to the blood. Congenital atresia of the bile ducts, obstruction brought on by cholelithiasis, inflammation of the liver, or tumors all end in posthepatic jaundice. The kind of jaundice current in an individual could additionally be indicated by will increase in the serum bilirubin level and modifications in the stools. For example, serum levels of unconjugated bilirubin (indirectreacting) are elevated in prehepatic jaundice, whereas posthepatic jaundice outcomes from increased quantities of conjugated bilirubin (direct) in the blood. In patients with liver illness, each intrahepatic and posthepatic jaundice could additionally be current as a result of inflammation or infection each impairs hepatocyte perform and obstructs the bile canaliculi, resulting in elevations in the blood of each unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin. In individuals with posthepatic jaundice, the obstruction prevents bile from coming into the gut, interfering with digestion and resulting in a light-colored stool. Also, the bile salts that enter the blood and tissues as bile backs up trigger irritation and pruritus (itching) of the pores and skin. Phototherapy is effective in gentle varieties, whereby publicity to ultraviolet mild promotes the conjugation of bilirubin. It may be idiopathic (fatty liver) or outcome from a neighborhood infection (viral hepatitis), from an infection elsewhere within the body. Mild irritation impairs hepatocyte perform, whereas more severe inflammation and necrosis could result in obstruction of blood and bile flow in the liver and impaired liver cell operate. Given the various features of the liver, damage to the liver cells has intensive results within the body. Fortunately, the liver has an excellent useful reserve and wonderful regenerative powers. Both the hepatocytes and the liver seem swollen, and diffuse necrosis may be present. With extreme inflammation, biliary stasis may develop, leading to backup of bile in to the blood. Some cases present a few manifestations but not jaundice; in other circumstances fulminant hepatitis develops with huge necrosis and liver failure. Depending on the severity of the irritation, the hepatic cells could regenerate, or fibrous scar tissue could kind within the liver. Scar tissue usually obstructs the channels used for blood and bile circulate, interfering with the unique group of the liver lobule, and leading to additional injury from ischemia. Chronic irritation happens with hepatitis B, C, and D and is defined as persistent inflammation and necrosis of the liver for more than 6 months.
Syndromes
- Tularemia
- Smoking
- Wheezing
- Watery eyes
- Cleft lip or palate
- Seizures
- Extreme pain when you move the affected area (for example, a person with compartment syndrome in the foot or lower leg will have severe pain when moving the toes up and down)
- CT scan of the head
- Europe
Buy flonase once a day
The new worldwide rhabdomyosarcoma classification, its progenitors, and issues past morphology. Paratesticular spindle cell rhabdomyosarcoma recognized by nice needle aspiration cytology: A case report. Rhabdomyosarcoma: cytogenetics of five cases using fine-needle aspiration samples and evaluation of the literature. Findings in fourteen fine needle aspiration biopsy specimens and one pleural fluid specimen. Cytohistologic correlations in angiosarcoma together with basic and epithelioid variants: the Institute Curie expertise. The clinical use of fine needle aspiration cytology for analysis and administration of youngsters with neuroblastic tumours. Fine needle aspiration cytology in the prognosis and administration of children and adolescents with Ewing sarcoma and peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Fine needle aspiration cytology in prognosis and management of childhood small round cell tumours. Cytogenetic characterisation of Ewing tumors utilizing nice needle aspiration samples, a 10-year experience and review of the literature. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors using morphology, immunocytochemistry and mutational analysis of c-kit. Fine-needle aspiration of synovial sarcoma: criteria for analysis: retrospective examination of 37 cases, including ancillary diagnostics. Aspiration cytology of pulmonary small cell variant of poorly-differentiated synovial sarcoma metastatic from the tongue: a case report. The advanced cytological features of synovial sarcoma in fantastic needle aspirates, an analysis of 4 illustrative instances. Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction on nice needle aspirates for rapid detection of translocations in synovial sarcoma. Fine needle aspiration cytology and core biopsy within the analysis of alveolar soft part sarcoma presenting with lung metastases. Cytologic features of clear cell sarcoma (malignant melanoma) of sentimental parts: a examine of fantastic needle aspirates and exfoliative specimens. Clear cell sarcoma diagnosis by fine-needle aspiration: cytologic, histologic, and ultrastructural features; potential pitfalls; and literature review. Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma with neuroendocrine differentiation: a case report with fine-needle aspiration biopsy, histopathology, electron microscopy, and cytogenetics. Malignant rhabdoid tumor of the liver identified by fantastic needle aspiration cytology. Intraabdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor: Cytopathologic finding in two cases. Intraabdominal desmoplastic small round cell tumor: report of a case with nice needle aspiration, cytologic analysis and molecular affirmation. Chondroblastoma of bone: use of fine-needle aspiration biopsy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. Low risk of recurrence of enchondroma and low grade chondrosarcoma in extremities. Light and electron-microscopic examination of fine-needle aspiration within the preoperative diagnosis of cartilaginous tumours. Potential sampling error in fine-needle aspiration biopsy of dedifferentiated chondrosarcoma: a report of 4 circumstances. Fineneedle aspiration of spinal osteoblastoma in a patient with lymphangiomatosis. Small cell osteosarcoma of the ribs: immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural examine with literature evaluation. Chordoma: prognosis by fine-needle aspiration with histologic, immunocytochemical, and ultrastructural affirmation. Fine needle aspiration biopsy of soppy tissue sarcomas: utility and diagnostic challenges. The role of fine needle aspiration biopsy in the preliminary prognosis of pediatric bone and delicate tissue tumors: an institutional experience.
Purchase flonase 50 mcg on line
Fat emboli are more widespread in patients with fractures of the pelvis or long bones such as the femur, significantly when the fracture website has not been properly immobilized throughout transportation instantly after the damage. Fat emboli journey to the lungs (see Chapter 19), the place they trigger obstruction, intensive inflammation, and respiratory misery syndrome, they usually might disseminate in to the systemic circulation as properly. Frequently the first indications of a fats embolus are behavioral changes, confusion, and disorientation associated with cerebral emboli, in combination with respiratory misery and extreme hypoxia. Fractures in or close to the joint might have long-term residual effects, such as osteoarthritis or stunted progress if the epiphyseal plate is broken in a child. Signs and symptoms In some instances a fracture is clearly present, as in patients with compound fractures or an apparent deformity. Swelling, tenderness on the site, or altered sensation is present but could occur with any kind of damage. In some circumstances, particularly with compound or a number of fractures, ache is delayed when nerve operate on the website is lost briefly. Pain outcomes from direct damage to the nerves by the trauma and from pressure and irritation as a result of the accrued blood and inflammatory response. Severe pain may cause shock with pallor, diaphoresis, hypotension, and tachycardia. Treatment Immediate splinting and immobilization of the fracture site is important to minimize the risk of problems. If essential, discount of the fracture is carried out to restore the bones to their normal position. Closed discount is accomplished by exerting strain and traction; open discount requires surgical procedure. During surgical procedure, devices such as pins, plates, rods, or screws may be positioned to repair the fragments in place; any necrotic or foreign materials is removed, and the bone ends are aligned and carefully approximated. This pressure maintains the alignment of the bones, prevents muscle spasm, and immobilizes the limb. During the healing interval, workouts are helpful to restrict muscle atrophy in the immobilized space, preserve good circulation, and minimize joint stiffness or contractures. Splint for help and immobilize for transport, including joints above and beneath the fracture. Dislocations trigger appreciable gentle tissue damage, together with damage to the ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels as the bone is pulled away from the joint. Treatment consists of reduction to return the dislocated bone to its normal place, immobilization throughout healing, and remedy to maintain joint mobility. Ligaments and tendons help the bones in a joint and may easily be torn when extreme pressure is exerted on a joint. In some instances, the ligaments or tendons could be utterly separated from their bony attachments, a problem known as avulsion. Sprains and strains are quite painful and are accompanied by tenderness, marked swelling, and infrequently discoloration as a outcome of hematoma formation. Diagnosis requires x-rays and other checks to rule out the presence of a fracture and determine the extent of the injury. After a tear occurs, irritation after which granulation tissue develop on the website. Collagen fibers are fashioned that create links with the remaining tendon or ligament, and finally the healing mass is sure together with fibrous tissue. Usually one bone is out of position, whereas the opposite stays in its regular location. If the bone is only partially displaced, with partial loss of contact between the surfaces, the harm is termed subluxation. Stress on a tendon within the early stage will reopen the tear and lead to the development of extreme fibrous tissue within the tendon and thus less energy, shortening, and decreased flexibility on the joint. With extreme damage to the tendons and ligaments, surgical restore may be essential. Surgery may be required to repair tears, take away damaged tissue, or replace joints.
Buy cheap flonase 50mcg on line
Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Food and fluid are taken in to the body by way of the mouth, where the initial part of mechanical breakdown and digestion takes place, and are then stored in the abdomen, where processing continues. Salivary secretions from the parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands enter the mouth through the salivary ducts, moisturizing and lubricating (with mucins) the meals particles and facilitating the passage of stable material down the esophagus to the stomach. Saliva also contains the enzyme amylase, which begins the digestion of carbohydrate within the mouth (Table 20-1). The tongue and cheeks facilitate the movement and mixing of the food in the mouth. Chewing is normally considered a voluntary action, however reflex chewing can happen if voluntary control is misplaced. When meals is prepared to be swallowed, the tongue pushes the bolus or ball of food back to the pharyngeal wall, where receptors of the trigeminal and glossopharyngeal nerves relay the data to the swallowing center in the medulla. Because the reflex is activated at this level, swallowing (or deglutition) turns into an involuntary activity. The pressure on this sphincter usually prevents reflux of gastric contents again up the esophagus. The complete tube is lined with mucous membrane and is closed, except when swallowing is in progress. The abdomen is an expansible muscular sac that acts as a reservoir for meals and fluid. The wall of the stomach consists of three easy muscle layers- longitudinal and circular layers and an additional oblique muscle layer-plus the mucosa and submucosa. Constant mixing and churning of food occurs as secretions are added from the gastric glands. These secretions dilute the gastric contents, or chyme, and initiate the digestion of protein. The gastric glands situated in the fundus of the stomach include parietal cells that secrete hydrochloric acid and chief cells that secrete pepsinogen, which is converted to the energetic form, pepsin, by the action of hydrochloric acid. Intrinsic issue, required for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the ileum, is also produced by the parietal cells (see Chapter 17 for discussion of pernicious anemia). The gastric secretions act as a defensive mechanism because of the extremely acidic pH (around 2), which destroys many microorganisms that enter the stomach from the resident flora within the mouth or from meals or utensils. Also, enteroendocrine cells in the glands secrete a wide selection of chemicals, crucial of which is the hormone gastrin, which is released when food enters the abdomen and then stimulates the parietal and chief cells. Depending to some extent on the kind of food ingested, gastric emptying proceeds slowly, with small amounts of chyme (1 to three mL) passing intermittently through the pyloric sphincter in to the duodenum. Secretions from the liver and the exocrine pancreas are added to the chyme in the duodenum by way of the ampulla of Vater and duodenal papilla. It is a big organ covered by a fibrous capsule, distention of which causes a boring, aching pain. The liver cells can regenerate, but when the organizational construction of the lobule, with its unique arrangement of blood vessels and bile ducts, is altered by necrosis and scar tissue, the regenerated areas may not be functional. The hepatocytes, or liver cells, are arranged in lobules, and each lobule has plates of cells radiating from central veins, which ultimately drain blood back in to the general circulation via the hepatic veins and inferior vena cava. Channels or sinusoids crammed with blood from two sources pass between the plates of hepatocytes. Entering the sinusoid is blood from branches of the hepatic artery, carrying oxygen to the liver cells; venous blood from the portal vein, which transports nutrients absorbed from the stomach and intestines (hepatic portal circulation); as nicely as from the pancreas and spleen. The arterial and venous blood combine and move slowly through the sinusoids, allowing the hepatocytes to do their jobs. The sinusoids are lined with endothelial cells and Kupffer cells, which remove and phagocytose any overseas materials and micro organism from the digestive tract earlier than the blood enters the general circulation. As blood flows through the sinusoids, many substances are exchanged to facilitate liver features. Many blood elements corresponding to iron or amino acids are monitored, and people which were depleted because the blood circulates through the body are changed.
Cheap flonase online mastercard
Many methods are acceptable, including sharp excision with a scalpel, rotary d�bridement, loop electrocautery as described by Guernsey,35 and laser ablation with a carbon dioxide laser. Treatment proceeds supraperiosteally to stop publicity of underlying palatal bone. Subsequently, placement of a tissue conditioner and a denture reline is useful to minimize patient discomfort. Hypermobile Tissue When excess cellular unsupported tissue remains after successful alveolar ridge restoration, or when cell tissue exists in the presence of a preserved alveolar ridge, elimination of this tissue is the remedy of selection. Sharp excision parallel to the defect in a supraperiosteal fashion permits for removing of cell tissue to a suitable level. Beveled incisions may be needed to mix the excision with surrounding adjoining tissues and keep continuity to the surrounding gentle tissue. Impressions for prosthesis fabrication ought to proceed after a 3- to 4-week interval to allow for sufficient soft tissue transforming. In instances in which denture flange extension is anticipated, the clinician must be cautious to protect the vestibule when undermining for soft tissue closure. The peak of this attachment varies from individual to particular person; nevertheless, in dentate people, frenum attachments not often cause an issue. In edentulous people, frenum attachments could intervene with match and stability, produce discomfort, and dislodge the overlying prostheses. Local anesthetic infiltration is performed in a regional style that avoids direct infiltration in to the frenum itself; such an infiltration distorts the anatomy and leads to misidentification of the frenum. Eversion of the lip additionally helps one determine the anatomical frenum and assists with the excision. An elliptical incision across the proposed frenum is accomplished in a supraperiosteal trend. Sharp dissection of the frenum utilizing curved scissors removes mucosa and underlying connective tissue resulting in a broad base of periosteum hooked up to the underlying bone. Once tissue margins are Fibrous Inflammatory Hyperplasia Fibrous inflammatory hyperplasia is commonly the outcomes of an ill-fitting denture that produces underlying irritation of the mucosa and eventual fibrous proliferation leading to affected person discomfort and a decreased fit of the overlying prosthesis. Early management consists mainly of adjustment of the offending denture flange with an related delicate reline of the prosthesis. In most circumstances, laser ablation with a carbon dioxide laser is the strategy of choice. When the therapy of huge lesions would end in vital scarring and obliteration of the vestibule, sharp excision with undermining of the adjacent mucosa and reapproximation of the tissues is most well-liked. Again, maintenance of a supraperiosteal aircraft with repositioning of mucosal edges permitting for subsequent granulation is most well-liked over approximation of wound edges that ends in the alteration of vestibular depth. This is achieved with local anesthetic infiltrated in to the proposed tissue mattress, which is closed provided that essential with resorbable sutures. After elimination of the hemostat, an incision is created by way of the world previously closed throughout the hemostat. The edges of the incision are undermined, and the wound edges are approximated and closed with a operating resorbable suture, burying the knots to minimize affected person discomfort. Sutures ought to encounter the periosteum, especially on the depth of the vestibule, to maintain alveolar ridge height. This additionally reduces hematoma formation and permits for the preservation of alveolar anatomy. In the Z-plasty method, excision of the connective tissue is completed much like that described previously. The two flaps are ultimately undermined and rotated to shut the preliminary vertical incision horizontally. By using the transposition flaps, this technique nearly will increase vestibular depth and must be used when alveolar peak is in question. Wide-based frenum attachments could finest be handled with a localized vestibuloplasty approach. Superior repositioning of the mucosa is completed, and the wound margin is sutured to the underlying periosteum on the depth of the vestibule.
Buy cheap flonase 50 mcg online
For instance, an annular lesion within the rectosigmoid area, the place the fecal mass is relatively strong, causes partial obstruction with dilation of the proximal colon. Vague cramping ache, small flat pellets or "ribbon" stool, and a feeling of incomplete emptying are common indicators of most cancers in this location. An unexplained change in bowel habits, corresponding to alternating diarrhea and constipation, may be an indication of malignancy. Bleeding could additionally be indicated by occult blood or melena if it arises from the proximal colon. Frank (red) blood and mucus on or near the floor of the stool usually signify bleeding from a lesion within the rectum. Treatment Colorectal cancer is handled by surgical elimination of the concerned space, normally requiring a colostomy, an artificial opening in to the stomach wall the place feces may be frequently collected in a bag. Current suggestions are for the use of two medication in a protocol that will embrace oral medication in addition to intravenous drugs. A new drug remedy cetuximab, targets growth issue indicators liable for cell replica. Describe, within the order during which they develop, each stage of the ache seen with acute appendicitis, together with the situation and sort of ache and the explanation for it. Define the term diverticulitis and explain how diverticula develop and turn into infected. Depending on the trigger and site, obstruction may manifest as an acute downside or a steadily creating situation. For example, twisting of the gut might cause sudden whole obstruction, whereas a tumor results in progressive obstruction. Mechanical obstructions are those resulting from tumor, adhesions, hernias, or different tangible obstructions. Functional, or adynamic, obstructions result from neurologic impairment, similar to spinal wire injury or lack of propulsion in the intestine, and are sometimes referred to as paralytic ileus. Although the end result may be the same, these types manifest somewhat differently and require totally different therapy. Pathophysiology When mechanical obstruction of the flow of intestinal contents happens, a sequence of events develops. Gases and fluids accumulate in the area proximal to the blockage, distending the gut. Gases arise primarily from swallowed air, but in addition from bacterial exercise in the intestine. Increasingly strong contractions of the proximal intestine occur in an effort to move the contents onward. The increasing strain in the lumen results in extra secretions entering the gut and likewise compresses the veins in the wall, preventing absorption, as the intestinal wall turns into edematous. The intestinal distention results in persistent vomiting with further loss of fluid and electrolytes. Ischemia and necrosis of the intestinal wall eventually result in decreased innervation and cessation of peristalsis. The obstruction promotes speedy reproduction of intestinal bacteria, some of which produce endotoxins. As the affected intestinal wall becomes necrotic and more permeable, intestinal micro organism or toxins can leak in to the peritoneal cavity (peritonitis) or the blood supply (bacteremia and septicemia). In time, perforation of the necrotic segment could occur, resulting in generalized peritonitis. Functional obstruction or paralytic ileus often results from neurologic impairment. Peristalsis ceases and distention of the gut occurs as fluids and electrolytes accumulate in the gut. Intussusception Colon narrowed by scar tissue Diverticulum crammed with feces Inflammation E. Severe vomiting from distention and pain results in dehydration and electrolyte imbalance Vomitus 5. Distention causes increased peristalsis to force contents previous obstruction, leading to colicky pain 6.
References
- Allander T, Tammi MT, Eriksson M, et al. Cloning of a human parvovirus by molecular screening of respiratory tract samples. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:12891-1Bastien N, Brandt K, Dust K, et al. Human bocavirus infection, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:848-850.
- McHugh LG, Milberg JA, Whitcome ME, et al. Recovery of function in survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;150:90-4.
- Tasaki O, Goodwin CW, Saitoh D, et al. Effects of burns on inhalation injury. J Trauma. 1997;43:603-607.
- Chang WC, Hung YC, Li TC, et al: Short course of prophylactic antibiotics in laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy, J Reprod Med 50(7):524n 528, 2005.