Dr Daniel Conway
- Dept of Anaesthesia
- Manchester Royal Infirmary
- Manchester
Ondansetron dosages: 8 mg, 4 mg
Ondansetron packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Buy generic ondansetron canada
Sinuses cut back the load of the skull and increase the depth of the voice by serving as resonant sound chambers. The frontal (fruntal) bone forms the anterior portion of the skull above the eyes, together with the forehead, the roof of the nasal cavity, and the roofs of the orbits (bony sockets) of the eyes. On the higher margin of every orbit, the frontal bone is marked by a supraorbital foramen (or supraorbital notch in some skulls) through which blood vessels and nerves pass to the tissues of the brow. Within the frontal bone are two frontal sinuses, one above each eye close to the midline (fig. The frontal bone is a single bone in adults, nevertheless it develops in two elements (see fig. These halves grow collectively and usually utterly fuse by the fifth or sixth 12 months of life. One parietal (pah-rie-tal) bone is situated on all sides of the skull just behind the frontal bone. They are fused at the midline along the sagittal suture, and so they meet the frontal bone along the coronal suture. The occipital (ok-sipi-tal) bone joins the parietal bones alongside the lambdoid (lamdoid) suture. A massive opening on its lower surface is the foramen magnum, where the inferior part of the brainstem connects with the spinal cord. Rounded processes referred to as occipital condyles, positioned on each side of the foramen magnum, articulate with the first vertebra (atlas) of the vertebral column. A temporal (tempor-al) bone on all sides of the skull joins the parietal bone alongside a squamous suture. Located close to the inferior margin is a gap, the exterior acoustic (auditory) meatus, which leads inward to components of the ear. The temporal bones additionally house the internal ear structures and have depressions known as the mandibular fossae (glenoid fossae) that articulate with condyles of the mandible. Below each external acoustic meatus are two projections-a rounded mastoid process and a protracted, pointed styloid course of (see fig. The mastoid process supplies an attachment for sure muscle tissue of the neck, whereas the styloid course of anchors muscles associated with the tongue and pharynx. An opening near the mastoid process, the carotid canal, transmits the internal carotid artery. An opening between the temporal and occipital bones, the jugular foramen, accommodates the interior jugular vein (fig. A zygomatic process projects anteriorly from the temporal bone within the region of the exterior acoustic meatus. It joins the temporal strategy of the zygomatic bone and helps type the prominence of the cheek, the zygomatic arch (fig. The sphenoid (sfenoid) bone is wedged between a number of different bones within the anterior portion of the skull (fig. It consists of a central half and two winglike constructions that stretch laterally toward each side of the skull. This bone helps type the bottom of the skull, the perimeters of the skull, and the flooring and sides of the orbits. In this despair lies the pituitary gland, which hangs from the bottom of the mind by a stalk. These lie facet by aspect and are separated by a bony septum that tasks downward into the nasal cavity. It consists of two lots, one on both sides of the nasal cavity, joined horizontally by thin cribriform (kribri-form) plates. These plates form a half of the roof of the nasal cavity, and nerves related to the sense of scent cross through tiny openings (olfactory foramina) in them. A perpendicular plate projects downward in the midline from the cribriform plates to type most of the nasal septum. Delicate, scroll-shaped plates known as the superior nasal concha (kongkah) and the center nasal concha project inward from the lateral parts of the ethmoid bone towards the perpendicular plate. The mucous membranes, in turn, begin moistening, warming, and filtering air because it enters the respiratory tract. The lateral portions of the ethmoid bone comprise many small areas, the ethmoidal air cells, that collectively kind the ethmoidal sinus (see fig. Facial Skeleton the facial skeleton consists of 13 immovable bones and a movable decrease jawbone.

Cheap 8mg ondansetron
In the gastric glands, specialized cells carefully associated with the parietal cells secrete the hormone somatostatin, which inhibits acid secretion. These parasympathetic impulses additionally stimulate sure stomach cells, mainly in the pyloric area, to launch a peptide hormone known as gastrin, which will increase the secretory activity of gastric glands (fig. Furthermore, parasympathetic impulses and gastrin promote launch of histamine from gastric mucosal cells, which, in turn, stimulates additional gastric secretion. Gastric secretion occurs in three stages-the cephalic, gastric, and intestinal phases. The cephalic part begins earlier than food reaches the abdomen and presumably even earlier than eating. In this stage, parasympathetic reflexes working through the vagus nerves stimulate gastric secretion at the style, smell, sight, or thought of meals. The gastric phase of gastric secretion, which accounts for most of the secretory activity, starts when meals enters the stomach. The presence of meals and the distension of the abdomen wall trigger the stomach to launch gastrin, which stimulates production of more gastric juice. As food enters the abdomen and mixes with gastric juice, the pH of the contents rises, which boosts gastrin secretion. For the abdomen to secrete hydrochloric acid, hydrogen ions are actively transported into the stomach. Negatively charged chloride ions, attracted by the positively charged hydrogen ions, transfer from the blood into the stomach. Following a meal, the blood focus of bicarbonate ions increases, and the urine excretes extra bicarbonate ions. The intestinal part of gastric secretion begins when food leaves the abdomen and enters the small gut. When food first contacts the intestinal wall, it stimulates intestinal cells to release a hormone, intestinal gastrin, that briefly enhances gastric gland secretion. His intensive injuries eventually healed, however a gap, called a fistula, was left, permitting observers to look at his abdomen in motion. Army surgeon, William beaumont, spent eight years watching food digesting in the stomach, and noted how the abdomen lining modified within the process. A colleague who repeated the experiment developed an ulcer and required antibiotics. After a decade of debate, the medical community finally concurred that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, which thrives underneath acidic circumstances, causes many cases of gastritis and peptic ulcers. A quick course of antibiotics and acid-lowering medication has replaced lifelong remedies. This coating is especially essential as a outcome of pepsin can digest the proteins of stomach tissues, in addition to those in foods. As extra food strikes into the small intestine, a sympathetic reflex triggered by acid in the upper a part of the small intestine inhibits secretion of gastric juice from the abdomen wall. Similarly, fats within the small intestine stimulate intestinal cells to release intestinal somatostatin, which inhibits release of gastric juice. Overall, these actions decrease gastric secretion and motility because the small intestine fills with food. The stomach absorbs only small volumes of water and certain salts, as well as sure lipid-soluble medicine. Mixing and emptying actions Food stretches the smooth muscle layers of the abdomen wall. The abdomen may enlarge, but its muscle layers maintain their tone, and inside strain of the stomach normally is unchanged. When an individual eats greater than the abdomen can comfortably hold, the internal stress might rise sufficient to stimulate ache receptors. Following a meal, the blending movements of the abdomen wall assist in producing a semifluid paste of food particles and gastric juice known as chyme (ki m).
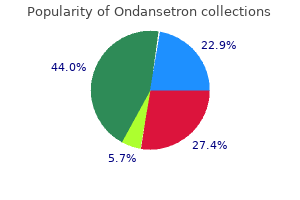
Cheap 8 mg ondansetron with mastercard
The tympanic membrane vibrates forwards and backwards in response to sound waves, reproducing the vibrations of the sound-wave supply. It is bounded by the tympanic membrane laterally and the internal ear medially and homes three small bones called auditory ossicles (awdi-tore osi-klz). The three auditory ossicles, called the malleus, the incus, and the stapes, are attached to the wall of the tympanic cavity by tiny ligaments and are coated by mucous membrane. These bones bridge the tympanic membrane and the internal ear, transferring vibrations between these elements. Specifically, the malleus is hooked up to the tympanic membrane, helping to keep its conical shape. The malleus vibrates the incus, and the incus passes the movement on to the stapes. Ligaments hold the stapes to an opening within the wall of the tympanic cavity known as the oval window (fig. Vibration of the stapes, which acts like a piston on the oval window, transfers the vibrations to a fluid inside the inside ear. Also, as a result of the ossicles switch vibrations from the large floor of the tympanic membrane to a a lot smaller space at the oval window, the vibrational force strengthens as it travels from the outer to the inside ear. As a result, the strain (per square millimeter) that the stapes applies on the oval window is about twenty-two occasions greater than that which sound waves exert on the tympanic membrane. The middle ear also has two small skeletal muscles connected to the auditory ossicles which would possibly be controlled by a reflex. One of them, the tensor tympani, is inserted on the medial surface of the malleus and is anchored to the cartilaginous wall of the auditory tube. The different muscle, the stapedius, is connected to the posterior side of the stapes and the internal wall of the tympanic cavity. These muscular tissues are the effectors within the tympanic reflex, which is elicited in about one-tenth of a second after a loud, exterior sound. As a outcome, the bridge of ossicles in the middle ear turns into extra rigid, decreasing its effectiveness in transferring vibrations to the internal ear. The tympanic reflex reduces pressure from loud sounds that may in any other case injury the hearing receptors. Ordinary vocal sounds additionally elicit the tympanic reflex, such as when an individual speaks or sings. This action muffles the lower frequencies of such sounds, enhancing the listening to of upper frequencies, that are widespread in human vocal sounds. In addition, the tensor tympani muscle maintains pressure on the tympanic membrane. This tube allows air to cross between the tympanic cavity and the skin of the body by the use of the throat (nasopharynx) and mouth. The perform of the auditory tube becomes noticeable throughout speedy change in altitude. As a person descends from a excessive altitude, the air stress on the outside of the tympanic membrane steadily will increase. This might push the tympanic membrane inward, out of its regular place, impairing listening to. When the air stress difference on the edges of the tympanic membrane is nice enough, some air might drive its method up by way of the auditory tube into the middle ear. This equalizes the strain on either side of the tympanic membrane, which moves again into its regular place, inflicting a popping sound as regular hearing returns. A reverse motion of air ordinarily occurs when a person ascends from a low altitude. The auditory tube is normally closed by valvelike flaps within the throat, which can inhibit air actions into the middle ear. Swallowing, yawning, or chewing assist in opening the flaps and might hasten equalization of air strain. Signs of a middle ear infection (otitis media) in a toddler include irritability, fever, and tugging on the painful ear. Using an instrument known as an otoscope reveals a purple and bulging tympanic membrane.
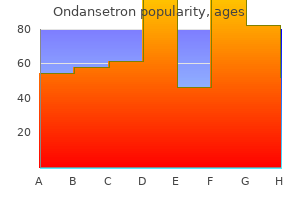
Order ondansetron 4 mg
As it passes between the medial malleolus and the heel, the posterior tibial artery divides into the medial and lateral plantar arteries. Branches from these arteries provide blood to tissues of the heel, instep, and toes. The largest department of the posterior tibial artery is the fibular artery, which extends downward alongside the fibula and contributes to the anastomosis of the ankle. Veins from the Upper Limb and Shoulder A set of deep veins and a set of superficial ones drain the upper limb. The deep veins typically parallel the arteries in every region and have related names. Deep venous drainage of the higher limbs begins within the digital veins that drain into pairs of radial veins and ulnar veins, which merge to type a pair of brachial veins. They also talk with the deep vessels of the upper limb, providing many alternate pathways through which the blood can leave the tissues (fig. They arise from anastomoses within the palm and wrist on the ulnar and radial sides, respectively. The basilic (bah-silik) vein passes alongside the again of the forearm on the ulnar side for a distance and then curves forward to the anterior surface beneath the elbow. The cephalic (se-falik) vein courses upward on the lateral facet of the higher limb from the hand to the shoulder. Unlike the arterial pathways, those of the venous system are troublesome to observe as a result of the smaller vessels generally connect in irregular networks. These veins typically parallel the courses of named arteries, and many bear the same names as their arterial counterparts. For example, the renal vein parallels the renal artery, and the widespread iliac vein accompanies the common iliac artery. The veins that carry the blood from the lungs and myocardium again to the center have been described. The veins from all the other parts of the physique converge into two main vessels, the superior and inferior venae cavae, which lead to the best atrium. Veins from the Brain, Head, and Neck the external jugular (jugu-lar) veins drain blood from the face, scalp, and superficial areas of the neck. These vessels descend on either facet of the neck, passing over the sternocleidomastoid muscles and beneath the platysma. The internal jugular veins, that are considerably larger than the external jugular veins, come up from many veins and venous sinuses of the mind and from deep veins in parts of the face and neck. They descend by way of the neck beside the common carotid arteries and likewise join the subclavian veins. These unions of the interior jugular and subclavian veins type giant brachiocephalic veins on both sides. These vessels then merge in the mediastinum and provides rise to the superior vena cava, which enters the proper atrium. A lung most cancers, enlarged lymph node, or an aortic aneurysm can compress the superior vena cava, interfering with return of blood from the higher physique to the heart. This produces pain; shortness of breath; distension of veins draining into the superior vena cava; and swelling of tissues in the face, head, and higher limbs. The proper and left ascending lumbar veins, with tributaries that include vessels from the lumbar and sacral regions, additionally hook up with the azygos system. Veins from the stomach Viscera Veins transport blood directly to the atria of the heart, except for portal veins, corresponding to those that drain the abdominal viscera (fig. They originate in the capillary networks of the stomach, intestines, pancreas, and spleen and transport blood from these organs via a hepatic portal (portal) vein to the liver (fig. This unique venous pathway is called the hepatic portal system, which permits blood to flow from the gastrointestinal organs to the liver earlier than returning to the guts. It regulates blood glucose concentration by polymerizing extra glucose into glycogen for storage or by breaking down glycogen into glucose when blood glucose focus drops beneath normal.

Purchase ondansetron 4mg online
Stem cells are present in grownup organs and migrate from the bone marrow to replace broken cells. As cells specialize, they express different units of genes that provide their distinct traits. It is a fast, orderly multistep process that begins when a cell surface receptor receives a signal to die. Caspases start a sequence response that cuts up the cell into membranebounded items. Apoptosis and mitosis are synchronized throughout growth, maturation, and growing older. What attribute of cell membranes could explain why fat-soluble substances similar to chloroform and ether rapidly have an effect on cells How might this effect clarify why smokers have an elevated incidence of coughing and respiratory infections Which process-diffusion, osmosis, or filtration-is used in the following situations The urea focus in the dialyzing fluid of an artificial kidney is decreased. For experimental stem cell therapy, state the a half of a cell reprogrammed to perform like that of a stem cell and stimulated to differentiate in a particular means. Reports within the media about stem cells normally state that they "turn into any kind of cell in the physique. Connect Integrated Activity Can you predict the impact illnesses or drugs may need on the cell membrane or organelles Anatomy & Physiology Revealed go more in depth into the human physique by viewing components of a cell underneath a microscope and viewing animations of the cell cycle. Many metabolic reactions occur one after the opposite in a sequence, with the merchandise of one response serving as starting materials for the following. In anabolism (a h-nabo-liz-em), small molecules are constructed up into larger ones, requiring power. In catabolism (ka tabo-liz-em), bigger molecules are damaged down into smaller ones, releasing power. About 60% of the energy launched as large molecules are dismantled escapes as heat. The remainder of the energy is used to build molecules and to drive varied actions of the cell. Dehydration synthesis also hyperlinks glycerol and fatty acid molecules in fat cells (adipose tissue) to kind triglyceride molecules. For example, a kind of anabolic course of known as dehydration synthesis (dehi-drashun sinthe-sis) joins many easy sugar molecules (monosaccharides) to type bigger molecules of glycogen, which store energy in their chemical bonds. When a runner eats pasta the night before a race, digestion breaks down the plant-based complicated carbohydrates within the food to monosaccharides. These smaller molecules are absorbed into the bloodstream, which carries the energy-rich molecules to physique cells. Here, dehydration synthesis joins the monosaccharides to form glycogen, which stores vitality that the runner might have later, because the finish line nears. Using a mat, a trainer might lead a client through a sequence of workout routines to strengthen the core stomach muscle tissue. Personal trainers are inclined to be outgoing, friendly individuals who take pleasure in helping others become bodily match. When dehydration synthesis unites two amino acid molecules, a peptide bond forms between a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom, leading to a dipeptide molecule (arrows pointing to the right). The results of this reaction is three water molecules and a single fats molecule whose glycerol and fatty acid parts are sure by shared oxygen atoms. In cells, dehydration synthesis also builds protein molecules by joining amino acid molecules.
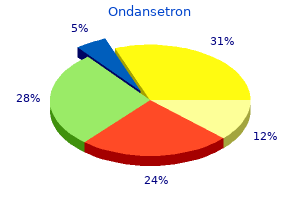
Order genuine ondansetron
Among probably the most fascinating aspects of nervous system function are the abilities of the brain to store recollections and to process aware thought. All of these things are achieved by neurons working in a lot the identical means, however serving different features throughout the mind, the spinal wire, or the peripheral nerves. This is the chapter by which your brain gets to find out about itself and the opposite components of the nervous system! It oversees many aspects of physiology, similar to sensation and perception, movement, and considering. The brain contains the 2 cerebral hemispheres, the diencephalon, the brainstem, and the cerebellum, all described in detail in section eleven. The mind incorporates about one hundred billion (1011) multipolar neurons as nicely as countless branches of the axons by which these neurons talk with each other and with neurons elsewhere within the nervous system. In the brain, the outer layers of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum are largely grey matter. White matter, representing interconnecting axons, is found deeper, with islands of grey matter situated throughout. In the spinal cord, in distinction, gray matter (the cell bodies of neurons) is discovered extra centrally, with white matter extra peripheral and consisting of axons extending as a lot as the brain or down from the brain. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull, and the spinal cord occupies the vertebral canal in the vertebral column. Beneath these bony coverings, membranes known as meninges, located between the bone and the soft tissues of the nervous system, protect the mind and spinal twine (fig. It attaches to the within of the cranial cavity and forms the internal periosteum of the surrounding skull bones (see reference plate 13, p. In some areas, the dura mater extends inward between lobes of the brain and forms supportive and protective partitions (table 11. In different areas, the dura mater splits into two layers, forming channels called dural sinuses, shown in determine 11. Venous blood flows via these channels because it returns from the mind to vessels resulting in the guts. The dura mater continues into the vertebral canal as a robust, tubular sheath that surrounds the spinal cord. It is attached to the cord at regular intervals by a band of pia mater (denticulate ligaments) that extends the length of the spinal cord on either side. The dural sheath terminates as a blind sac on the level of the second sacral vertebra, under the tip of the spinal twine. This house accommodates blood vessels, free connective tissue, and adipose tissue that pad the spinal cord. A blow to the head could rupture some blood vessels related to the mind, and the escaping blood could gather beneath the dura mater. This situation, called subdural hematoma, can increase strain between the rigid bones of the cranium and the gentle tissues of the mind. Unless the accumulating blood is promptly evacuated, compression of the brain may lead to practical losses or even dying. The fluid protects the brain and spinal wire by absorbing forces which may in any other case jar and injury their delicate tissues. The pia mater is skinny and accommodates many nerves, in addition to blood vessels that nourish the underlying cells of the brain and spinal cord. The pia mater is connected to the surfaces of those organs and follows their irregular contours, passing over the high areas and dipping into the depressions. A visit from an occupational therapist tremendously improved each his independence and his spirit. The occupational therapist confirmed the man tips on how to proceed to use a relaxation room sink by supporting his weight on his arms, and tips on how to use mirrors to compensate for his neck stiffness. The therapist was comforting and practical as he confirmed the man how to repurpose steel salad tongs to hold rest room paper to look after his rest room wants. An occupational therapist helps a person keep regular activities whereas battling a disease, damage, disability, or different limitation. The therapist may instruct members of the family and caregivers on the way to help the patient. More than 5 million individuals have such injuries, that are categorized as gentle, gentle repetitive, or severe.

Order ondansetron
Clinical signs of retinal detachment include visual sensations generally described as a "shower of pepper" or floaters. These are caused by red blood cells extravasated from the capillary vessels which have been injured in the course of the retinal tear or detachment. In addition, some people describe sudden flashes of sunshine, as well as a "internet" or "veil" in entrance of the attention along side the onset of floaters. If not repositioned quickly, the indifferent area of the retina will endure necrosis, leading to blindness. More commonly, because the vitreous body ages (in the sixth and seventh many years of life), it tends to shrink and draw back from the neural retina, which causes single or multiple tears in the neural retina. An argon laser is usually used to repair retinal detachment by photocoagulating the sides of the detachment and producing scar tissue. This method prevents the retina from additional detachment and facilitates the repositioning of photoreceptor cells. This image reveals a view of the fundus of the proper eye in a patient with retinal detachment. The central retinal vessels emerging from the optic disc are in focus, but in the area of the retinal detachment they seem to be out of focus. This is as a result of of the reality that the area of retinal detachment is elevated (note a quantity of ridges and shadows) and is positioned anterior to the aircraft of focus of the ophthalmoscope. The disease causes loss of central imaginative and prescient, although peripheral vision stays unaffected. These newly shaped, skinny, fragile vessels regularly leak and produce exudates and hemorrhages within the house simply beneath the retina, leading to fibrosis and scarring. These changes are liable for the progressive loss of central vision over a short while. In this procedure, the retina is detached, translocated, and reattached in a new location, away from the choroid neovascular tissue. Conventional laser therapy is then applied to destroy pathologic vessels with out destroying central imaginative and prescient. Note that central imaginative and prescient is absent because of the changes within the macula area of the retina. To maximize their remaining imaginative and prescient, people with this condition are instructed to use eccentric fixation of their eyes. The nonphotosensitive area (nonvisual part), located anterior to the ora serrata, lines the inside aspect of the ciliary physique and the posterior floor of the iris (this portion of the retina is described within the sections on the iris and ciliary body). The web site where the optic nerve joins the retina known as the optic disc or optic papilla. Because the optic disc is devoid Retina the retina represents the innermost layer of the eye. It consists of two primary layers: � � the neural retina or retina proper is the inner layer that incorporates the photoreceptor cells. In relative terms, the fovea is the area of the retina that contains the very best concentration and most precisely ordered association of the visual elements. Layers of the Retina Ten layers of cells and their processes represent the retina. The two layers could also be separated mechanically within the preparation of histologic specimens. Separation of the layers, Before discussing the ten layers of the retina, it is important to determine the forms of cells found there. This identification will aid in understanding the practical relationships of the cells. Studies of the retina in primates have recognized a minimal of 15 forms of neurons that form at least 38 various sorts of synapses. Layer of rods and cones-contains the outer and internal segments of photoreceptor cells 3. Outer nuclear layer-contains the cell our bodies (nuclei) of retinal rods and cones 5. Outer plexiform layer-contains the processes of retinal rods and cones and processes of the horizontal, amacrine, and bipolar cells that connect with them 6. Inner plexiform layer-contains the processes of horizontal, amacrine, bipolar, and ganglion cells that connect with each other eight. Layer of optic nerve fibers-contains processes of ganglion cells that lead from the retina to the mind 10.
References
- Hirama M, Atsuta R, Mitani K, et al. Lymphangioleiomyomatosis diagnosed by immunocytochemical and genetic analysis of lymphangioleiomyomatosis cell clusters found in chylous pleural effusion. Intern Med 2007;46(18):1593-6.
- Nitzold A, Khattab A, Eggers J: Microemboli in aortic valve replacement, Exp Rev Cardiovasc Therap 4:853, 2006.
- Knepper M, Gamba G. Urine concentration and dilution. In: Brenner B, ed. Brenner & Rector's The Kidney. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2004.
- Husmann, D.A., McLorie, G.A., Churchill, B.M. Nonrefluxing colonic conduits: a long-term life-table analysis. J Urol 1989;142:1201-1203.
- Peiper SC, Wang ZX, Neote K, et al: The Duffy antigen/receptor for chemokines (DARC) is expressed in endothelial cells of Duffy-negative individuals who lack the erythrocyte receptor, J Exp Med 181:1311-1317, 1995.
- Deyton LR. FDA tobacco product regulations: a powerful tool for tobacco control. Public Health Rep 2011;126(2):167-169.
- Mills EJ, Bansback N, Ghement I, et al. Multiple treatment comparison meta-analyses: a step forward into complexity. Clin Epidemiol. 2011;3:193-202.
- Hatanaka K, Tsuta K, Watanabe K, Sugino K, Uekusa T. Primary pulmonary adenocarcinoma with enteric differentiation resembling metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a report of the second case negative for cytokeratin 7.